Disseminated tuberculosis manifesting as pulmonary, meningeal and spinal tuberculosis in an immunocompetent patient
- PMID: 23239776
- PMCID: PMC4544991
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2012-007778
Disseminated tuberculosis manifesting as pulmonary, meningeal and spinal tuberculosis in an immunocompetent patient
Abstract
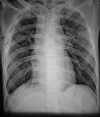
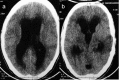
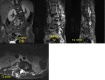
Disseminated tuberculosis is characterised by concurrent tubercular involvement of two or more non-contiguous organs. It is an unusual presentation of tuberculosis, especially in the absence of immunodeficiency. We describe a young, immunocompetent patient who presented with fever, cough, headache, diplopia and paraparesis. On examination, the patient had positive Kernig's sign, right third cranial nerve palsy and bilateral sixth cranial nerve palsy, bilateral lower limb weakness and crepititions on lung auscultation bilaterally. Chest radiogram revealed bilateral pulmonary tuberculosis. CT of brain showed hydrocephalus and MRI of spine showed collapse of lumbar vertebrae with paravertebral cold abscess. Sputum microscopy was positive for acid fast bacilli, cerebrospinal fluid analysis was suggestive of tubercular meningitis and CT-guided biopsy of the vertebral lesions revealed caseating granulomas with acid fast bacilli. The patient received antitubercular therapy with initial treatment with steroids and he improved clinically at the end of a 9-month treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Sharma SK, Mohan A. Extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Indian J Med Res 2004;120:316–53. - PubMed
-
- Vohra R, Kang HS, Dogra S, et al. Tuberculous osteomyelitis. Bone Joint Surg Br 1997;79:562. - PubMed
-
- Bloch AB, Reider HL, Kelly GD, et al. The epidemiology of tuberculosis in the United States. Sem Resp Infect 1989;4:157–70. - PubMed
-
- Kalita J, Misra UK. Tuberculous meningitis with pulmonary miliary tuberculosis: a clinicoradiological study. Neurol India 2004;52:194–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
