The emerging role of the mitochondrial-derived peptide humanin in stress resistance
- PMID: 23239898
- PMCID: PMC3705736
- DOI: 10.1530/JME-12-0203
The emerging role of the mitochondrial-derived peptide humanin in stress resistance
Abstract
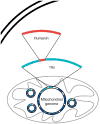
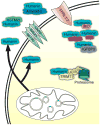
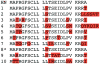
The discovery of humanin, a novel, mitochondrial-derived peptide, has created a potentially new category of biologically active peptide. As more research unravels the endogenous role of humanin as well as its potential pharmacological use, its role in stress resistance has become clearer. Humanin protects cells from oxidative stress, serum starvation, hypoxia, and other insults in vitro and also improves cardiovascular disease as well as Alzheimer's disease in vivo. In this review, we discuss the emerging role of humanin in stress resistance and its proposed mechanism of action.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oxidative Damage? Not a Problem! The Characterization of Humanin-like Mitochondrial Peptide in Anoxia Tolerant Freshwater Turtles.Protein J. 2021 Feb;40(1):87-107. doi: 10.1007/s10930-020-09944-7. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Protein J. 2021. PMID: 33387248
-
Role of humanin, a mitochondrial-derived peptide, in cardiovascular disorders.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020 Aug-Sep;113(8-9):564-571. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2020.03.020. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32680738 Review.
-
Cardio-protective role of Humanin in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2022 Feb;1866(2):130066. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2021.130066. Epub 2021 Dec 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2022. PMID: 34896254 Review.
-
Humanin prevents brain mitochondrial dysfunction in a cardiac ischaemia-reperfusion injury model.Exp Physiol. 2016 Jun 1;101(6):697-707. doi: 10.1113/EP085749. Exp Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27059110
-
The role of humanin in natural stress tolerance: An underexplored therapeutic avenue.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2022 Jan;1866(1):130022. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2021.130022. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2022. PMID: 34626747 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms by which different functional states of mitochondria define yeast longevity.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Mar 11;16(3):5528-54. doi: 10.3390/ijms16035528. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25768339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic stress signalling: understanding the cell non-autonomous control of proteostasis.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Mar;15(3):211-7. doi: 10.1038/nrm3752. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24556842 Free PMC article.
-
The Mitochondrial-Derived Peptide MOTS-c Attenuates Oxidative Stress Injury and the Inflammatory Response of H9c2 Cells Through the Nrf2/ARE and NF-κB Pathways.Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2022 Oct;13(5):651-661. doi: 10.1007/s13239-021-00589-w. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2022. PMID: 34859377
-
Humanin Protects RPE Cells from Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis by Upregulation of Mitochondrial Glutathione.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 26;11(10):e0165150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165150. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27783653 Free PMC article.
-
The Mitochondrial-Derived Peptide (MOTS-c) Interacted with Nrf2 to Defend the Antioxidant System to Protect Dopaminergic Neurons Against Rotenone Exposure.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;60(10):5915-5930. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03443-3. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37380822
References
-
- Bachar AR, Scheffer L, Schroeder AS, Nakamura HK, Cobb LJ, Oh YK, Lerman LO, Pagano RE, Cohen P, Lerman A. Humanin is expressed in human vascular walls and has a cytoprotective effect against oxidized LDL-induced oxidative stress. Cardiovascular Research. 2010;88:360–366. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq191. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

