PlcRa, a new quorum-sensing regulator from Bacillus cereus, plays a role in oxidative stress responses and cysteine metabolism in stationary phase
- PMID: 23239999
- PMCID: PMC3519770
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051047
PlcRa, a new quorum-sensing regulator from Bacillus cereus, plays a role in oxidative stress responses and cysteine metabolism in stationary phase
Abstract
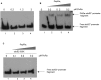
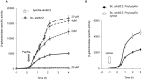
We characterized a new quorum-sensing regulator, PlcRa, which is present in various members of the B. cereus group and identified a signaling heptapeptide for PlcRa activity: PapRa(7). We demonstrated that PlcRa is a 3D structural paralog of PlcR using sequence analysis and homology modeling. A comparison of the transcriptomes at the onset of stationary phase of a ΔplcRa mutant and the wild-type B. cereus ATCC 14579 strain showed that 68 genes were upregulated and 49 genes were downregulated in the ΔplcRa mutant strain (>3-fold change). Genes involved in the cysteine metabolism (putative CymR regulon) were downregulated in the ΔplcRa mutant strain. We focused on the gene with the largest difference in expression level between the two conditions, which encoded -AbrB2- a new regulator of the AbrB family. We demonstrated that purified PlcRa bound specifically to the abrB2 promoter in the presence of synthetic PapRa(7), in an electrophoretic mobility shift assay. We further showed that the AbrB2 regulator controlled the expression of the yrrT operon involved in methionine to cysteine conversion. We found that the ΔplcRa mutant strain was more sensitive to hydrogen peroxide- and disulfide-induced stresses than the wild type. When cystine was added to the culture of the ΔplcRa mutant, challenged with hydrogen peroxide, growth inhibition was abolished. In conclusion, we identified a new RNPP transcriptional regulator in B. cereus that activated the oxidative stress response and cysteine metabolism in transition state cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
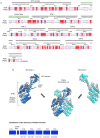
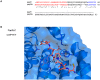
Similar articles
-
Quorum sensing in Bacillus thuringiensis is required for completion of a full infectious cycle in the insect.Toxins (Basel). 2014 Jul 31;6(8):2239-55. doi: 10.3390/toxins6082239. Toxins (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25089349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The signaling peptide PapR is required for the activity of the quorum-sensor PlcRa in Bacillus thuringiensis.Microbiology (Reading). 2020 Apr;166(4):398-410. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000883. Epub 2020 Jan 28. Microbiology (Reading). 2020. PMID: 32067627
-
Cereulide synthesis in emetic Bacillus cereus is controlled by the transition state regulator AbrB, but not by the virulence regulator PlcR.Microbiology (Reading). 2009 Mar;155(Pt 3):922-931. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.024125-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2009. PMID: 19246763
-
The YvfTU two-component system is involved in plcR expression in Bacillus cereus.BMC Microbiol. 2008 Oct 16;8:183. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-8-183. BMC Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18925929 Free PMC article.
-
The osmotic stress response operon betIBA is under the functional regulation of BetI and the quorum-sensing regulator AnoR in Acinetobacter nosocomialis.J Microbiol. 2020 Jun;58(6):519-529. doi: 10.1007/s12275-020-0186-1. Epub 2020 May 27. J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32462489 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and utilization of peptide-based quorum sensing modulators in Gram-positive bacteria.Org Biomol Chem. 2020 Sep 30;18(37):7273-7290. doi: 10.1039/d0ob01421d. Org Biomol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32914160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quorum sensing in Bacillus thuringiensis is required for completion of a full infectious cycle in the insect.Toxins (Basel). 2014 Jul 31;6(8):2239-55. doi: 10.3390/toxins6082239. Toxins (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25089349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Food Poisoning Toxins of Bacillus cereus.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jan 28;13(2):98. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020098. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33525722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting agr- and agr-Like quorum sensing systems for development of common therapeutics to treat multiple gram-positive bacterial infections.Sensors (Basel). 2013 Apr 18;13(4):5130-66. doi: 10.3390/s130405130. Sensors (Basel). 2013. PMID: 23598501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation and characteristics of a novel N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase gene involved in Bacillus thuringiensis mother cell lysis.J Bacteriol. 2013 Jun;195(12):2887-97. doi: 10.1128/JB.00112-13. Epub 2013 Apr 19. J Bacteriol. 2013. PMID: 23603740 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stenfors Arnesen LP, Fagerlund A, Granum PE (2008) From soil to gut: Bacillus cereus and its food poisoning toxins. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32: 579–606. - PubMed
-
- Piggot PJ, Hilbert DW (2004) Sporulation of Bacillus subtilis . Curr Opin Microbiol 7: 579–586. - PubMed
-
- Price CW, Fawcett P, Ceremonie H, Su N, Murphy CK, et al. (2001) Genome-wide analysis of the general stress response in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 41: 757–774. - PubMed
-
- Zuber P (2009) Management of oxidative stress in Bacillus . Annu Rev Microbiol 63: 575–597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

