Quantification of the host response proteome after mammalian reovirus T1L infection
- PMID: 23240068
- PMCID: PMC3519901
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051939
Quantification of the host response proteome after mammalian reovirus T1L infection
Abstract
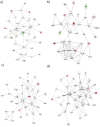
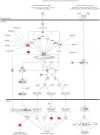
All viruses are dependent upon host cells for replication. Infection can induce profound changes within cells, including apoptosis, morphological changes, and activation of signaling pathways. Many of these alterations have been analyzed by gene arrays to measure the cellular "transcriptome." We used SILAC (stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture), combined with high-throughput 2-D HPLC/mass spectrometry, to determine relative quantitative differences in host proteins at 6 and 24 hours after infecting HEK293 cells with reovirus serotype 1 Lang (T1L). 3,076 host proteins were detected at 6 hpi, of which 132 and 68 proteins were significantly up or down regulated, respectively. 2,992 cellular proteins, of which 104 and 49 were up or down regulated, respectively, were identified at 24 hpi. IPA and DAVID analyses indicated proteins involved in cell death, cell growth factors, oxygen transport, cell structure organization and inflammatory defense response to virus were up-regulated, whereas proteins involved in apoptosis, isomerase activity, and metabolism were down-regulated. These proteins and pathways may be suitable targets for intervention to either attenuate virus infection or enhance oncolytic potential.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Clarke P, Tyler KL (2003) Reovirus-induced apoptosis: A minireview. Apoptosis 8: 141–150. - PubMed
-
- Salgado M, Lopez-Romero P, Callejas S, Lopez M, Labarga P, et al. (2011) Characterization of host genetic expression patterns in HIV-infected individuals with divergent disease progression. Virology 411: 103–112. - PubMed
-
- Nesvizhskii AI, Aebersold R (2005) Interpretation of shotgun proteomic data: the protein inference problem. Mol Cell Proteomics 4: 1419–1440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

