Crossword puzzles: self-learning tool in pharmacology
- PMID: 23240102
- PMCID: PMC3518804
- DOI: 10.1007/s40037-012-0033-0
Crossword puzzles: self-learning tool in pharmacology
Abstract
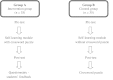
Students of the second professional MBBS course of the Indian medical curriculum (II MBBS) perceive pharmacology as a 'Volatile Subject' because they often find it difficult to remember and recall drug names. We evaluated the usefulness of crossword puzzles as a self-learning tool to help pharmacology students to remember drug names. We also measured the students' satisfaction with this learning method. This was an open-label randomized, two-arm intervention study, conducted with II MBBS students (n = 70), randomly selected and assigned to two groups A (n = 35) and B (n = 35). Two self-learning modules containing crossword puzzles with antihypertensive and antiepileptic drug terms were prepared and pre-validated. Hard copies of both crossword puzzles were administered to Group A (Intervention group) on two different occasions. One hour was allotted to solve a puzzle. Students were allowed to refer to their textbooks. Group B (Control group) underwent the self-learning module without the crossword puzzles. In both groups, pre- and post-test knowledge was assessed. Students' perceptions of the crossword puzzles were assessed using a pre-validated 10-item questionnaire. Responses to items 1-8 were recorded using a 5-point Likert scale. Responses to item 9 were recorded on a 10-point rating scale while item 10 was an open-ended question. The crossword completion index was 92.86 %. In group A, the average pre-test score was 6.09 whereas the average post-test score was 12.87 (p < 0.05). In group B, average pre- and post-test scores were 6.03 and 9.74, respectively. A significant difference (p < 0.001) was observed between the post-test scores of the two groups. The absolute learning gain was 33.9 % in Group A and 18.55 % in Group B. The response rate for the questionnaire was 100 %. Of the students, 71.43 % strongly agreed that crossword puzzles enhanced their knowledge of antihypertensive and antiepileptic drugs and were helpful for remembering and recalling the drug names, 60 % students found it challenging and a good problem solving activity and 85.71 % students opined that it was a good self-learning, recreational activity. The test scores improved when crossword puzzles, designed to improve retention of drug names, were incorporated in the self-study modules of pharmacology training. Students rated the crossword puzzles as a challenging and effective self-learning tool. Students' acceptability for crossword puzzles further favours their usefulness as a self-learning tool. The crossword puzzle is an effective tool for 'recreational learning' and can be used as an active learning strategy to promote self-directed learning.
Keywords: Active learning; Crossword puzzles; Pharmacology; Recreational learning; Self-learning.
Figures
References
-
- Sethuraman KR. Teaching-learning methods—II. In: Ananthakrishnan A, Sethuraman KR, Kumar S, editors. Medical education principles and practice. 2. Pondicherry: Alumni Association of NTTC, JIPMER; 2000. pp. 51–60.
-
- Dandekar SP. Teaching learning methods. In: Bhuiyan PS, Rege NN, Supe AV, editors. The art of teaching medical students. 2. Mumbai: MET Cell, Seth GSMC and KEM, Hospital; 2002. pp. 95–102.
-
- Saxena A, Nesbitt R, Pahwa P, Mills S. Crossword puzzles: active learning in undergraduate pathology and medical education. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133(9):1457–1462. - PubMed
-
- Ritzko JM, Robinson S. Using games to increase active learning. J Coll Teach Learn. 2006;3(6):45–50.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources