A review of the efficacy and safety of oral antidiabetic drugs
- PMID: 23241069
- PMCID: PMC3977601
- DOI: 10.1517/14740338.2013.752813
A review of the efficacy and safety of oral antidiabetic drugs
Abstract
Introduction: Additional oral antidiabetic agents to metformin, sulfonylureas (SU) and thiazolidinediones (TZD) are approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
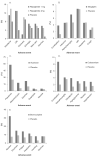
Areas covered: The efficacy and safety of metformin, SUs, TZDs, dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-4) inhibitors, meglitinide analogs, α-glucosidase inhibitors (AGIs), bile-acid sequestrants (BAS) and bromocriptine will be reviewed.
Expert opinion: Several new oral agents have been approved for type 2 diabetes management in recent years. It is important to understand the efficacy and safety of these medications in addition to the older agents to best maximize oral drug therapy for diabetes. Of the recently introduced oral hypoglycemic/antihyperglycemic agents, the DPP-4 inhibitors are moderately efficacious compared with mainstay treatment with metformin with a low side-effect profile and have good efficacy in combination with other oral agents and insulin. They are a recommended alternative when metformin use is limited by gastrointestinal (GI) side effects or when SU treatment results in significant hypoglycemia or weight gain. Meglitinide analogs are limited by their frequent dosing, expense and hypoglycemia (repaglinide > nateglinide), while AGIs are also limited by their dosing schedule and GI side-effect profile. BAS and bromocriptine have the lowest efficacy with regard to HbA(1c) reduction, also are plagued by GI adverse reactions, but have a low risk of hypoglycemia.
Figures
References
-
- Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: A patient-centered approach. position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) Diabetologia. 2012;55:1577–96. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg RB, Kendall DM, Deeg MA, et al. A comparison of lipid and glycemic effects of pioglitazone and rosiglitazone in patients with type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1547–54. - PubMed
-
- Deeg MA, Buse JB, Goldberg RB, et al. Pioglitazone and rosiglitazone have different effects on serum lipoprotein particle concentrations and sizes in patients with type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:2458–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
