Structures of the Escherichia coli transcription activator and regulator of diauxie, XylR: an AraC DNA-binding family member with a LacI/GalR ligand-binding domain
- PMID: 23241389
- PMCID: PMC3561964
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks1207
Structures of the Escherichia coli transcription activator and regulator of diauxie, XylR: an AraC DNA-binding family member with a LacI/GalR ligand-binding domain
Abstract
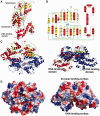
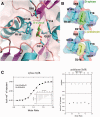
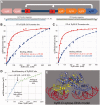
Escherichia coli can rapidly switch to the metabolism of l-arabinose and d-xylose in the absence of its preferred carbon source, glucose, in a process called carbon catabolite repression. Transcription of the genes required for l-arabinose and d-xylose consumption is regulated by the sugar-responsive transcription factors, AraC and XylR. E. coli represents a promising candidate for biofuel production through the metabolism of hemicellulose, which is composed of d-xylose and l-arabinose. Understanding the l-arabinose/d-xylose regulatory network is key for such biocatalyst development. Unlike AraC, which is a well-studied protein, little is known about XylR. To gain insight into XylR function, we performed biochemical and structural studies. XylR contains a C-terminal AraC-like domain. However, its N-terminal d-xylose-binding domain contains a periplasmic-binding protein (PBP) fold with structural homology to LacI/GalR transcription regulators. Like LacI/GalR proteins, the XylR PBP domain mediates dimerization. However, unlike LacI/GalR proteins, which dimerize in a parallel, side-to-side manner, XylR PBP dimers are antiparallel. Strikingly, d-xylose binding to this domain results in a helix to strand transition at the dimer interface that reorients both DNA-binding domains, allowing them to bind and loop distant operator sites. Thus, the combined data reveal the ligand-induced activation mechanism of a new family of DNA-binding proteins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The XylR variant (R121C and P363S) releases arabinose-induced catabolite repression on xylose fermentation and enhances coutilization of lignocellulosic sugar mixtures.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2019 Dec;116(12):3476-3481. doi: 10.1002/bit.27144. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2019. PMID: 31429933
-
Parallel evolution of ligand specificity between LacI/GalR family repressors and periplasmic sugar-binding proteins.Mol Biol Evol. 2003 Feb;20(2):267-77. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msg038. Mol Biol Evol. 2003. PMID: 12598694
-
Experimental evolution reveals an effective avenue to release catabolite repression via mutations in XylR.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jul 11;114(28):7349-7354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1700345114. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28655843 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic, structural and functional analyses of the LacI-GalR family of bacterial transcription factors.FEBS Lett. 1995 Dec 18;377(2):98-102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01344-x. FEBS Lett. 1995. PMID: 8543068 Review.
-
Allostery in the LacI/GalR family: variations on a theme.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2009 Apr;12(2):129-37. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2009.01.009. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19269243 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the role of the transcriptional regulator VirS in low pH-induced responses of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and identification of VirS inhibitors.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jun 28;294(26):10055-10075. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005312. Epub 2019 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31126988 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Mechanism of the Efflux Pumps Transcription Regulators From Pseudomonas aeruginosa Based on 3D Structures.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Jun 19;5:57. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00057. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 29971236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A conserved inhibitory interdomain interaction regulates DNA-binding activities of hybrid two-component systems in Bacteroides.mBio. 2024 Jul 17;15(7):e0122024. doi: 10.1128/mbio.01220-24. Epub 2024 Jun 6. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38842315 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic Gene Circuits for Regulation of Next-Generation Cell-Based Therapeutics.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Feb;11(8):e2309088. doi: 10.1002/advs.202309088. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38126677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Determination of Mutational Timing of Colistin-Resistance Genes through Klebsiella pneumoniae Evolution.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 12;15(1):270. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010270. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bruckner R, Titgemeyer F. Carbon catabolite repression in bacteria: choice of the carbon source and autoregulatory limitation of sugar utilization. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002;209:141–148. - PubMed
-
- Song S, Park C. Organization, regulation of the D-xylose operons in Escherichia coli K-12: XylR acts as a transcriptional activator. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998;163:255–261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

