The ABCG8 G574R variant, serum plant sterol levels, and cardiovascular disease risk in the Old Order Amish
- PMID: 23241408
- PMCID: PMC3817740
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.245480
The ABCG8 G574R variant, serum plant sterol levels, and cardiovascular disease risk in the Old Order Amish
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether long-term exposure to moderate elevations in plasma plant sterol levels increases risk for atherosclerosis.
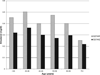
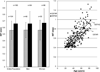
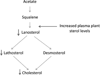
Methods and results: In Old Order Amish participants aged 18 to 85 years, with (n=110) and without (n=181) 1 copy of the ABCG8 G574R variant, we compared mean plasma levels of plant sterols and cholesterol precursors and carotid intima-media wall thickness. Carriers of a single 574R allele had increased plant sterol levels (eg, 35%-37% higher plasma levels of sitosterol, campesterol, and stigmasterol) and increased plant sterol/cholesterol ratios (P<0.001 for all). 574R carriers had significantly decreased levels of lathosterol and lanosterol, precursors in a pathway for endogenous cholesterol synthesis, suggesting that plant sterols may alter regulation of genes involved in cholesterol synthesis. The G574R variant was not associated with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels. Compared with noncarriers, 574R carriers had decreased carotid intima-media wall thickness (0.62 versus 0.66 mm; age- and sex-adjusted P=0.03). Adjustment for body weight, blood pressure, and standard lipid measures (high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and triglycerides) did not alter this association.
Conclusions: Although the G574R variant is associated with moderately elevated plant sterol levels, carriers of the 574R allele had modestly lower levels of carotid wall thickness compared with noncarriers.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Timely diagnosis of sitosterolemia by next generation sequencing in two children with severe hypercholesterolemia.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Jul;262:71-77. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 4. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28521186
-
Genetic basis and hematologic manifestations of sitosterolemia in a group of Turkish patients.J Clin Lipidol. 2021 Sep-Oct;15(5):690-698. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2021.07.001. Epub 2021 Jul 10. J Clin Lipidol. 2021. PMID: 34304999
-
[Clinical, molecular genetic analysis, and treatment of 3 children with sitosterolemia].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2018 Jun 2;56(6):435-439. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2018.06.006. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29886606 Chinese.
-
Plant Sterols, Stanols, and Sitosterolemia.J AOAC Int. 2015 May-Jun;98(3):716-723. doi: 10.5740/jaoacint.SGEAjagbe. Epub 2015 May 4. J AOAC Int. 2015. PMID: 25941971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sitosterolemia presenting with severe hypercholesterolemia and intertriginous xanthomas in a breastfed infant: case report and brief review.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 May;99(5):1512-8. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3274. Epub 2014 Jan 1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24423340 Review.
Cited by
-
Familial aggregation of tobacco use behaviors among Amish men.Nicotine Tob Res. 2014 Jul;16(7):923-30. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntu006. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Nicotine Tob Res. 2014. PMID: 24583363 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characterization of familial hypercholesterolemia due to an amish founder mutation in Apolipoprotein B.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Mar 17;22(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02539-3. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 35300601 Free PMC article.
-
Phytosterols and Cardiovascular Risk Evaluated against the Background of Phytosterolemia Cases-A German Expert Panel Statement.Nutrients. 2023 Feb 6;15(4):828. doi: 10.3390/nu15040828. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36839186 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing and Complementary Mechanisms of Synergistic Action of Acori Tatarinowii Rhizoma and Codonopsis Radix for Alzheimer's Disease Based on Systems Pharmacology.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Jun 25;2020:6317230. doi: 10.1155/2020/6317230. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32802132 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol-Lowering Nutraceuticals Affecting Vascular Function and Cardiovascular Disease Risk.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018 May 25;20(7):53. doi: 10.1007/s11886-018-0994-7. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29802549 Review.
References
-
- Berge KE, Tian H, Graf GA, Yu L, Grishin NV, Schultz J, Kwiterovich P, Shan B, Barnes R, Hobbs HH. Accumulation of dietary cholesterol in sitosterolemia caused by mutations in adjacent ABC transporters. Science. 2000;290:1771–1775. - PubMed
-
- Patel SB, Salen G, Hidaka H, Kwiterovich PO, Stalenhoef AF, Miettinen TA, Grundy SM, Lee MH, Rubenstein JS, Polymeropoulos MH, Brownstein MJ. Mapping a gene involved in regulating dietary cholesterol absorption. The sitosterolemia locus is found at chromosome 2p21. J Clin Invest. 1998;102:1041–1044. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Graf GA, Yu L, Li WP, Gerard R, Tuma PL, Cohen JC, Hobbs HH. ABCG5 and ABCG8 are obligate heterodimers for protein trafficking and biliary cholesterol excretion. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:48275–48282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

