Human apolipoprotein A-II protects against diet-induced atherosclerosis in transgenic rabbits
- PMID: 23241412
- PMCID: PMC3673010
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300445
Human apolipoprotein A-II protects against diet-induced atherosclerosis in transgenic rabbits
Abstract
Objective: Apolipoprotein (apo) A-II is the second major apo of high-density lipoproteins, yet its pathophysiological roles in the development of atherosclerosis remain unknown. We aimed to examine whether apo A-II plays any role in atherogenesis and, if so, to elucidate the mechanism involved.
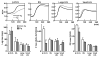
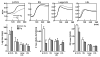
Methods and results: We compared the susceptibility of human apo A-II transgenic (Tg) rabbits to cholesterol diet-induced atherosclerosis with non-Tg littermate rabbits. Tg rabbits developed significantly less aortic and coronary atherosclerosis than their non-Tg littermates, while total plasma cholesterol levels were similar. Atherosclerotic lesions of Tg rabbits were characterized by reduced macrophages and smooth muscle cells, and apo A-II immunoreactive proteins were frequently detected in the lesions. Tg rabbits exhibited low levels of plasma C-reactive protein and blood leukocytes compared with non-Tg rabbits, and high-density lipoproteins of Tg rabbit plasma exerted stronger cholesterol efflux activity and inhibitory effects on the inflammatory cytokine expression by macrophages in vitro than high-density lipoproteins isolated from non-Tg rabbits. In addition, β-very-low-density lipoproteins of Tg rabbits were less sensitive to copper-induced oxidation than β-very-low-density lipoproteins of non-Tg rabbits.
Conclusions: These results suggest that enrichment of apo A-II in high-density lipoprotein particles has atheroprotective effects and apo A-II may become a target for the treatment of atherosclerosis.
Figures
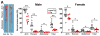
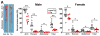
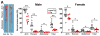



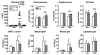
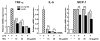
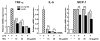

Comment in
-
Apolipoprotein A-II: still second fiddle in high-density lipoprotein metabolism?Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Feb;33(2):166-7. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300921. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23325471 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein CIII Deficiency Protects Against Atherosclerosis in Knockout Rabbits.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Sep;40(9):2095-2107. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314368. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32757647 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Hepatic Expression of Endothelial Lipase Inhibits Cholesterol Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia and Atherosclerosis in Transgenic Rabbits.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Jul;37(7):1282-1289. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309139. Epub 2017 May 25. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28546217 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Protects Against Atherosclerosis in Rabbits.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Jun;37(6):1068-1075. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309114. Epub 2017 Apr 20. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28428219 Free PMC article.
-
The role of dietary oxidized cholesterol and oxidized fatty acids in the development of atherosclerosis.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2005 Nov;49(11):1075-82. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200500063. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2005. PMID: 16270280 Review.
-
High-density lipoprotein and atherosclerosis: the role of antioxidant activity.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2012 Apr;14(2):101-7. doi: 10.1007/s11883-012-0235-2. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2012. PMID: 22441969 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Understanding of the Immunomodulatory Activities of High-Density Lipoproteins.Biomedicines. 2021 May 21;9(6):587. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9060587. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34064071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDL functionality in type 1 diabetes: enhancement of cholesterol efflux capacity in relationship with decreased HDL carbamylation after improvement of glycemic control.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Aug 12;21(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01591-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35962339 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sex hormones affect endothelial lipase-mediated lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Dec 23;18(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1175-4. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31870448 Free PMC article.
-
Speciated High-Density Lipoprotein Biogenesis and Functionality.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2016 May;18(5):25. doi: 10.1007/s11883-016-0572-7. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2016. PMID: 27005803 Review.
-
Small hepatitis B virus surface antigen (SHBs) induces dyslipidemia by suppressing apolipoprotein-AII expression through ER stress-mediated modulation of HNF4α and C/EBPγ.J Virol. 2024 Nov 19;98(11):e0123924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01239-24. Epub 2024 Oct 29. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39470210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gordon T, Castelli WP, Hjortland MC, Kannel WB, Dawber TR. High density lipoprotein as a protective factor against coronary heart disease. The Framingham Study. Am J Med. 1977;62:707–714. - PubMed
-
- Linsel-Nitschke P, Tall AR. HDL as a target in the treatment of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2005;4:193–205. - PubMed
-
- Chan DC, Ng TW, Watts GF. Apolipoprotein A-II: evaluating its significance in dyslipidaemia, insulin resistance, and atherosclerosis. Ann Med. 2012;44:313–324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

