Sequential engagement of FcεRI on Mast Cells and Basophil Histamine H(4) Receptor and FcεRI in Allergic Rhinitis
- PMID: 23241885
- PMCID: PMC3538893
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202049
Sequential engagement of FcεRI on Mast Cells and Basophil Histamine H(4) Receptor and FcεRI in Allergic Rhinitis
Abstract
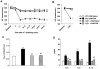
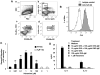
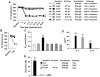
Histamine H(4) receptor (H(4)R)-deficient mice (H(4)R(-/-)), H(4)R antagonist-treated wild-type (WT) mice, and WT mice depleted of basophils failed to develop early (EPR) or late phase (LPR) nasal responses following allergen sensitization and challenge. Basophil transfer from WT but not H(4)R(-/-) mice restored the EPR and LPR in H(4)R(-/-) mice. Following passive sensitization with OVA-specific IgE, FcεRI(-/-) recipients of WT basophils plus OVA and histamine developed an EPR and LPR. OVA-IgE passively sensitized FcεRI(-/-) recipients of H(4)R(-/-) basophils and OVA and histamine challenge failed to develop an EPR or LPR, and basophils were not detected in nasal tissue. In contrast, recipients of basophils from IL-13(-/-) and IL-4(-/-)/IL-13(-/-) mice developed an EPR but not an LPR. These results demonstrate the development of allergic rhinitis proceeded in two distinct stages: histamine release from FcεRI-activated mast cells, followed by histamine-mediated recruitment of H(4)R-expressing basophils to the nasal cavity and activation through FcεRI.
Figures





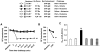

Similar articles
-
IL-3 but not monomeric IgE regulates FcεRI levels and cell survival in primary human basophils.Cell Death Dis. 2018 May 1;9(5):510. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0526-9. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29724998 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of IgE-mediated allergic reactions by pharmacologically targeting the circadian clock.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Apr;137(4):1226-1235. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.08.052. Epub 2015 Nov 11. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26559325
-
FcepsilonRI-alpha siRNA inhibits the antigen-induced activation of mast cells.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2009 Dec;8(4):177-83. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2009. PMID: 20404387
-
News in Cellular Allergology: A Review of the Human Mast Cell and Basophil Granulocyte Literature from January 2013 to May 2015.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2015;168(4):253-62. doi: 10.1159/000443960. Epub 2016 Feb 20. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26895271 Review.
-
The role of basophils in allergic disease.Eur Respir J Suppl. 1996 Aug;22:126s-131s. Eur Respir J Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8871057 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the Systemic Impact of Herbal Medicines on Allergic Rhinitis: A Network Pharmacological Approach.Life (Basel). 2024 Apr 25;14(5):553. doi: 10.3390/life14050553. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38792575 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Expression of Substance P and NK1R in CCR3+ and CD123+HLA-DR- Basophils Under Airway Allergic Conditions.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2022 Nov;14(6):687-712. doi: 10.4168/aair.2022.14.6.687. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36426398 Free PMC article.
-
Nasal sensitization with ragweed pollen induces local-allergic-rhinitis-like symptoms in mice.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 13;9(8):e103540. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103540. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25119881 Free PMC article.
-
Looking forward to new targeted treatments for chronic spontaneous urticaria.Clin Transl Allergy. 2017 Jan 10;7:1. doi: 10.1186/s13601-016-0139-2. eCollection 2017. Clin Transl Allergy. 2017. PMID: 28078079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intranasal exposure to monoclonal antibody Fab fragments to Japanese cedar pollen Cry j1 suppresses Japanese cedar pollen-induced allergic rhinitis.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 May;173(10):1629-38. doi: 10.1111/bph.13463. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26895546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, Zuberbier T, Baena-Cagnani CE, Canonica GW, Weel C van, Agache I, Aït-Khaled N, Bachert C, Blaiss MS, Bonini S, Boulet LP, Bousquet PJ, Camargos P, Carlsen KH, Chen Y, Custovic A, Dahl R, Demoly P, Douagui H, Durham SR, van Wijk RG, Kalayci O, Kaliner MA, Kim YY, Kowalski ML, Kuna P, Le LT, Lemiere C, Li J, Lockey RF, Mavale-Manuel S, Meltzer EO, Mohammad Y, Mullol J, Naclerio R, O’Hehir RE, Ohta K, Ouedraogo S, Palkonen S, Papadopoulos N, Passalacqua G, Pawankar R, Popov TA, Rabe KF, Rosado-Pinto J, Scadding GK, Simons FE, Toskala E, Valovirta E, van Cauwenberge P, Wang DY, Wickman M, Yawn BP, Yorgancioglu A, Yusuf OM, Zar H, Annesi-Maesano I, Bateman ED, Ben Kheder A, Boakye DA, Bouchard J, Burney P, Busse WW, Chan-Yeung M, Chavannes NH, Chuchalin A, Dolen WK, Emuzyte R, Grouse L, Humbert M, Jackson C, Johnston SL, Keith PK, Kemp JP, Klossek JM, Larenas-Linnemann D, Lipworth B, Malo JL, Marshall GD, Naspitz C, Nekam K, Niggemann B, Nizankowska-Mogilnicka E, Okamoto Y, Orru MP, Potter P, Price D, Stoloff SW, Vandenplas O, Viegi G, Williams D World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN, and AllerGen. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA2LEN and AllerGen) Allergy. 2008;63:8–160. - PubMed
-
- Marple BF. Targeting congestion in allergic rhinitis: the importance of intranasal corticosteroids. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008;29:232–240. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez-Trujillo V. Antihistamines treatment for allergic rhinitis: Different routes, different mechanisms? Allergy Asthma Proc. 2009;30:584–588. - PubMed
-
- Thurmond RL, Gelfand EW, Dunford PJ. The role of histamine H1 and H4 receptors in allergic inflammation: the search for new antihistamines. Nat Rev Drug Disc. 2008;7:41–53. - PubMed
-
- Jutel M, Akdis M, Akdis CA. Histamine, histamine receptors and their role in immune pathology. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009;39:1786–1800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

