Distribution and environmental persistence of the causative agent of white-nose syndrome, Geomyces destructans, in bat hibernacula of the eastern United States
- PMID: 23241985
- PMCID: PMC3568617
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02939-12
Distribution and environmental persistence of the causative agent of white-nose syndrome, Geomyces destructans, in bat hibernacula of the eastern United States
Abstract
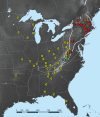
White-nose syndrome (WNS) is an emerging disease of hibernating bats caused by the recently described fungus Geomyces destructans. First isolated in 2008, the origins of this fungus in North America and its ability to persist in the environment remain undefined. To investigate the correlation between manifestation of WNS and distribution of G. destructans in the United States, we analyzed sediment samples collected from 55 bat hibernacula (caves and mines) both within and outside the known range of WNS using a newly developed real-time PCR assay. Geomyces destructans was detected in 17 of 21 sites within the known range of WNS at the time when the samples were collected; the fungus was not found in 28 sites beyond the known range of the disease at the time when environmental samples were collected. These data indicate that the distribution of G. destructans is correlated with disease in hibernating bats and support the hypothesis that the fungus is likely an exotic species in North America. Additionally, we examined whether G. destructans persists in infested bat hibernacula when bats are absent. Sediment samples were collected from 14 WNS-positive hibernacula, and the samples were screened for viable fungus by using a culture technique. Viable G. destructans was cultivated from 7 of the 14 sites sampled during late summer, when bats were no longer in hibernation, suggesting that the fungus can persist in the environment in the absence of bat hosts for long periods of time.
Figures
References
-
- Blehert DS, Hicks AC, Behr M, Meteyer CU, Berlowski-Zier BM, Buckles EL, Coleman JTH, Darling SR, Gargas A, Niver R, Okoniewski JC, Rudd RJ, Stone WB. 2009. Bat white-nose syndrome: an emerging fungal pathogen? Science 323:227 doi:10.1126/science.1163874 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gargas A, Trest MT, Christensen M, Volk TJ, Blehert DS. 2009. Geomyces destructans sp. nov. associated with bat white-nose syndrome. Mycotaxon 108:147–154
-
- Brooks RT. 2011. Declines in summer bat activity in central New England 4 years following the initial detection of white-nose syndrome. Biodivers. Conserv. 20:2537–2541
-
- Turner GG, Reeder DM, Coleman JTH. 2011. A five-year assessment of mortality and geographic spread of white-nose syndrome in North American bats and a look to the future. Bat Res. News 52:13–27
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

