An overview of thoracic actinomycosis: CT features
- PMID: 23242581
- PMCID: PMC3609961
- DOI: 10.1007/s13244-012-0205-9
An overview of thoracic actinomycosis: CT features
Abstract
Background: Thoracic actinomycosis is an uncommon, chronic suppurative bacterial infection caused by actinomyces species, especially Actinomyces israelii.
Methods: It is usually seen in immunocompetent patients with respiratory disorders, poor oral hygiene, alcoholism and chronic debilitating diseases.
Results: We illustrate the radiological manifestations of thoracic actinomycoses in various involved areas in the thorax.
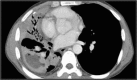
Conclusion: Thoracic actinomycosis can be radiologically divided into the parenchymal type, the airway type including bronchiectasis, the endobronchial form, and the mediastinum or chest wall involvement type.
Teaching points: • Important risk factors for thoracic actinomycosis are underlying respiratory disorders such as emphysema and chronic bronchitis. • Different CT patterns can be distinguished in thoracic actinomycosis: parenchymal, bronchiectatic, endobronchial and extrapulmonary. • Typical CT findings in the parenchymal pattern are a central low density within the parenchymal consolidation and adjacent pleural thickening.
Figures









References
-
- Russo TA. Agents of actinomycosis. In: Mandell GL, Bennet JE, Dolin R, editors. Principles and practice of infectious disease. 6. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone; 2005. pp. 2924–2934.
-
- Bartlett AH, Rivera AL, Krishnamurthy R, Baker CJ. Thoracic actinomycosis in children: case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2008;27(2):165–169. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

