A phase II study of UCN-01 in combination with irinotecan in patients with metastatic triple negative breast cancer
- PMID: 23242585
- PMCID: PMC3539064
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-012-2378-9
A phase II study of UCN-01 in combination with irinotecan in patients with metastatic triple negative breast cancer
Abstract
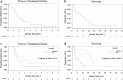
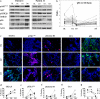
Mutations in TP53 lead to a defective G1 checkpoint and the dependence on checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1) for G2 or S phase arrest in response to DNA damage. In preclinical studies, Chk1 inhibition resulted in enhanced cytotoxicity of several chemotherapeutic agents. The high frequency of TP53 mutations in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC: negative for estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER2) make Chk1 an attractive therapeutic target. UCN-01, a non-selective Chk1 inhibitor, combined with irinotecan demonstrated activity in advanced TNBC in our Phase I study. The goal of this trial was to further evaluate this treatment in women with TNBC. Patients with metastatic TNBC previously treated with anthracyclines and taxanes received irinotecan (100-125 mg/m(2) IV days 1, 8, 15, 22) and UCN-01 (70 mg/m(2) IV day 2, 35 mg/m(2) day 23 and subsequent doses) every 42-day cycle. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and tumor specimens were collected. Twenty five patients were enrolled. The overall response (complete response (CR) + partial response (PR)) rate was 4 %. The clinical benefit rate (CR + PR + stable disease ≥6 months) was 12 %. Since UCN-01 inhibits PDK1, phosphorylated ribosomal protein S6 (pS6) in PBMC was assessed. Although reduced 24 h post UCN-01, pS6 levels rose to baseline by day 8, indicating loss of UCN-01 bioavailability. Immunostains of γH2AX and pChk1(S296) on serial tumor biopsies from four patients demonstrated an induction of DNA damage and Chk1 activation following irinotecan. However, Chk1 inhibition by UCN-01 was not observed in all tumors. Most tumors were basal-like (69 %), and carried mutations in TP53 (53 %). Median overall survival in patients with TP53 mutant tumors was poor compared to wild type (5.5 vs. 20.3 months, p = 0.004). This regimen had limited activity in TNBC. Inconsistent Chk1 inhibition was likely due to the pharmacokinetics of UCN-01. TP53 mutations were associated with a poor prognosis in metastatic TNBC.
Figures
References
-
- Kassam F, Enright K, Dent R, Dranitsaris G, Myers J, Flynn C, Fralick M, Kumar R, Clemons M. Survival outcomes for patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: implications for clinical practice and trial design. Clin Breast Cancer. 2009;9(1):29–33. doi: 10.3816/CBC.2009.n.005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

