Measuring tumor cycling hypoxia and angiogenesis using a side-firing fiber optic probe
- PMID: 23242854
- PMCID: PMC3702687
- DOI: 10.1002/jbio.201200187
Measuring tumor cycling hypoxia and angiogenesis using a side-firing fiber optic probe
Abstract
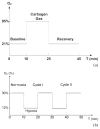
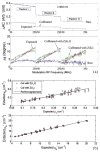
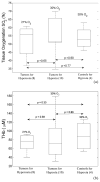
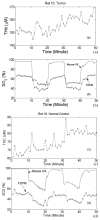
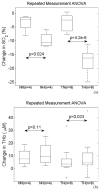
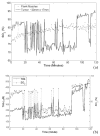
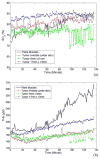
Hypoxia and angiogenesis can significantly influence the efficacy of cancer therapy and the behavior of surviving tumor cells. There is a growing demand for technologies to measure tumor hypoxia and angiogenesis temporally in vivo to enable advances in drug development and optimization. This paper reports the use of frequency-domain photon migration with a side-firing probe to quantify tumor oxygenation and hemoglobin concentrations in nude rats bearing human head/neck tumors administered with carbogen gas, cycling hypoxic gas or just room air. Significant increase (with carbogen gas breathing) or decrease (with hypoxic gas breathing) in tumor oxygenation was observed. The trend in tumor oxygenation during forced cycling hypoxia (CH) followed that of the blood oxygenation measured with a pulse oximeter. Natural CH was also observed in rats under room air. The studies demonstrated the potential of the technology for longitudinal monitoring of tumor CH during tumor growth or in response to therapy.
Keywords: Diffuse optical spectroscopy; cancer therapy; fiber optic sensor; tumor hypoxia and angiogenesis.
Copyright © 2014 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures




References
-
- Serganova I, Humm J, Ling C, Blasberg R. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(18):5260–5264. - PubMed
-
- Brey EM, King TW, Johnston C, McIntire LV, Reece GP, Patrick CW., Jr Microvasc Res. 2002;63(3):279–294. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Li CY, Moeller BJ, Yu D, Zhao Y, Dreher MR, Shan S, Dewhirst MW. Cancer Res. 2005;65(13):5498–5505. - PubMed
-
- Moeller BJ, Dreher MR, Rabbani ZN, Schroeder T, Cao Y, Li CY, Dewhirst MW. Cancer Cell. 2005;8(2):99–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

