A prospective study of plasma adiponectin and pancreatic cancer risk in five US cohorts
- PMID: 23243202
- PMCID: PMC3545904
- DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djs474
A prospective study of plasma adiponectin and pancreatic cancer risk in five US cohorts
Abstract
Background: The adipocyte-secreted hormone adiponectin has insulin-sensitizing and anti-inflammatory properties. Although development of pancreatic cancer is associated with states of insulin resistance and chronic inflammation, the mechanistic basis of the associations is poorly understood.
Methods: To determine whether prediagnostic plasma levels of adiponectin are associated with risk of pancreatic cancer, we conducted a nested case-control study of 468 pancreatic cancer case subjects and 1080 matched control subjects from five prospective US cohorts: Health Professionals Follow-up Study, Nurses' Health Study, Physicians' Health Study, Women's Health Initiative, and Women's Health Study. Control subjects were matched to case subjects by prospective cohort, year of birth, smoking status, fasting status, and month of blood draw. All samples for plasma adiponectin were handled identically in a single batch. Odds ratios were calculated with conditional logistic regression, and linearity of the association between adiponectin and pancreatic cancer was modeled with restricted cubic spline regression. All statistical tests were two-sided.
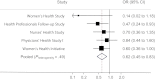
Results: Median plasma adiponectin was lower in case subjects versus control subjects (6.2 vs 6.8 µg/mL, P = .009). Plasma adiponectin was inversely associated with pancreatic cancer risk, which was consistent across the five prospective cohorts (P (heterogeneity) = .49) and independent of other markers of insulin resistance (eg, diabetes, body mass index, physical activity, plasma C-peptide). Compared with the lowest quintile of adiponectin, individuals in quintiles 2 to 5 had multivariable odds ratios ([ORs] 95% confidence intervals [CIs]) of OR = 0.61 (95% CI = 0.43 to 0.86), OR = 0.58 (95% CI = 0.41 to 0.84), OR = 0.59 (95% CI = 0.40 to 0.87), and OR = 0.66 (95% CI = 0.44 to 0.97), respectively (P (trend) = .04). Restricted cubic spline regression confirmed a nonlinear association (P (nonlinearity) < .01). The association was not modified by sex, smoking, body mass index, physical activity, or C-peptide (all P (interaction) > .10).
Conclusions: In this pooled analysis, low prediagnostic levels of circulating adiponectin were associated with an elevated risk of pancreatic cancer.
Figures

Comment in
-
Plasma adiponectin: a possible link between fat metabolism and pancreatic cancer risk.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013 Jan 16;105(2):79-80. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs522. Epub 2012 Dec 14. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013. PMID: 23243204 No abstract available.
References
-
- American Cancer Society Cancer facts & figures 2011. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2011.
-
- World Cancer Research Fund/American Institute for Cancer Research Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity, and the Prevention of Cancer: a Global Perspective. Washington DC: AICR; 2009.
-
- Maeda K, Okubo K, Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Matsubara K. cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apM1 (adipose most abundant gene transcript 1). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1996; 221(2):286–289 - PubMed
-
- Scherer PE, Williams S, Fogliano M, Baldini G, Lodish HF. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1995; 270(45):26746–26749 - PubMed
-
- Hu E, Liang P, Spiegelman BM. AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271(18):10697–10703 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01WH22110/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 97193/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL043851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- N01WH32108-9/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42107-26/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- CA047988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 34944/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32122/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA87969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- NCI K07 CA140790/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL080467/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA040360/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA127003/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA034944/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH24152/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HL043851/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH42129-32/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 26490/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32100-2/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL034595/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 WH022110/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 34595/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA124908/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA 40360/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA55075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL026490/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32105-6/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA047988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32111-13/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32118-32119/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080467/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA140790/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH32115/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA097193/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01WH44221/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

