A crucial role for p90RSK-mediated reduction of ERK5 transcriptional activity in endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 23243209
- PMCID: PMC3574639
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.116988
A crucial role for p90RSK-mediated reduction of ERK5 transcriptional activity in endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor for cardiovascular mortality by increasing endothelial cell (EC) dysfunction and subsequently accelerating atherosclerosis. Extracellular-signal regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) is activated by steady laminar flow and regulates EC function by increasing endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression and inhibiting EC inflammation. However, the role and regulatory mechanisms of ERK5 in EC dysfunction and atherosclerosis are poorly understood. Here, we report the critical role of the p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (p90RSK)/ERK5 complex in EC dysfunction in diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis.
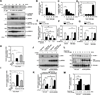
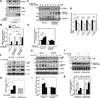
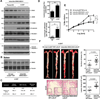
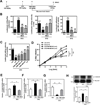
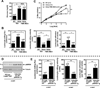
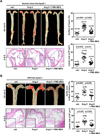
Methods and results: Inducible EC-specific ERK5 knockout (ERK5-EKO) mice showed increased leukocyte rolling and impaired vessel reactivity. To examine the role of endothelial ERK5 in atherosclerosis, we used inducible ERK5-EKO-LDLR(-/-) mice and observed increased plaque formation. When activated, p90RSK associated with ERK5, and this association inhibited ERK5 transcriptional activity and upregulated vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 expression. In addition, p90RSK directly phosphorylated ERK5 S496 and reduced endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression. p90RSK activity was increased in diabetic mouse vessels, and fluoromethyl ketone-methoxyethylamine, a specific p90RSK inhibitor, ameliorated EC-leukocyte recruitment and diminished vascular reactivity in diabetic mice. Interestingly, in ERK5-EKO mice, increased leukocyte rolling and impaired vessel reactivity were resistant to the beneficial effects of fluoromethyl ketone-methoxyethylamine, suggesting a critical role for endothelial ERK5 in mediating the salutary effects of fluoromethyl ketone-methoxyethylamine on endothelial dysfunction. Fluoromethyl ketone-methoxyethylamine also inhibited atherosclerosis formation in ApoE(-/-) mice.
Conclusions: Our study highlights the importance of the p90RSK/ERK5 module as a critical mediator of EC dysfunction in diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis formation, thus revealing a potential new target for therapeutic intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
p90RSK targets the ERK5-CHIP ubiquitin E3 ligase activity in diabetic hearts and promotes cardiac apoptosis and dysfunction.Circ Res. 2012 Feb 17;110(4):536-50. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.254730. Epub 2012 Jan 19. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22267842 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 SUMOylation antagonizes shear stress-induced antiinflammatory response and endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression in endothelial cells.Circ Res. 2008 Mar 14;102(5):538-45. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.156877. Epub 2008 Jan 24. Circ Res. 2008. PMID: 18218985
-
Disturbed flow-activated p90RSK kinase accelerates atherosclerosis by inhibiting SENP2 function.J Clin Invest. 2015 Mar 2;125(3):1299-310. doi: 10.1172/JCI76453. Epub 2015 Feb 17. J Clin Invest. 2015. PMID: 25689261 Free PMC article.
-
Disturbed-flow-mediated vascular reactive oxygen species induce endothelial dysfunction.Circ J. 2011;75(12):2722-30. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-11-1124. Epub 2011 Nov 10. Circ J. 2011. PMID: 22076424 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel mechanisms of endothelial mechanotransduction.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 Nov;34(11):2378-86. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303428. Epub 2014 Oct 9. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 25301843 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-374b induces endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and early lesion formation through the inhibition of MAPK7 signaling.J Pathol. 2019 Apr;247(4):456-470. doi: 10.1002/path.5204. Epub 2019 Jan 16. J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30565701 Free PMC article.
-
The Ser/Thr kinase p90RSK promotes kidney fibrosis by modulating fibroblast-epithelial crosstalk.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jun 21;294(25):9901-9910. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007904. Epub 2019 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31076505 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a Reliable Mouse Model for Cancer Therapy-Induced Cardiovascular Toxicity in Cancer Patients and Survivors.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018 Apr 5;5:26. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00026. eCollection 2018. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018. PMID: 29675417 Free PMC article.
-
LRP-1: functions, signaling and implications in kidney and other diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Dec 10;15(12):22887-901. doi: 10.3390/ijms151222887. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25514242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coordination of Cellular Localization-Dependent Effects of Sumoylation in Regulating Cardiovascular and Neurological Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;963:337-358. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-50044-7_20. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28197922 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim JA, Montagnani M, Koh KK, Quon MJ. Reciprocal relationships between insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: Molecular and pathophysiological mechanisms. Circulation. 2006;113:1888–1904. - PubMed
-
- Cai H, Harrison DG. Endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: The role of oxidant stress. Circ Res. 2000;87:840–844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL-088637/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111480/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM071434/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL108551/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-077789/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- PG/12/76/29852/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- GM-071434/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102746/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- PG/09/052/27833/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- P01 HL077789/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-064839/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL088637/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

