Transforming growth factor-β directly induces p53-up-regulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) during the rapid induction of apoptosis in myc-driven B-cell lymphomas
- PMID: 23243310
- PMCID: PMC3576124
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.410274
Transforming growth factor-β directly induces p53-up-regulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) during the rapid induction of apoptosis in myc-driven B-cell lymphomas
Abstract
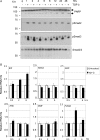
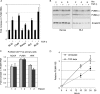
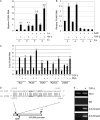
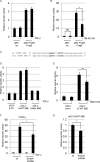
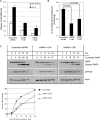
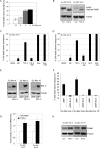
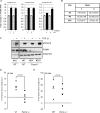
c-Myc transformed human Burkitt's lymphoma (BL) cells are highly sensitive to TGF-β-induced apoptosis. Previously we demonstrated that TGF-β-mediated cell death in BL cells is regulated via the mitochondrial intrinsic apoptosis pathway, which is dependent on the activation of BAX and/or BAK. TGF-β directly induces transcription of the BH3-only protein BIK and represses expression of the pro-survival factor BCL-X(L) but has no effect on the direct BAX/BAK "activators" BIM or BID (tBID). Here we show that TGF-β induces the BH3-only activator PUMA to aid induction of the intrinsic cell death pathway. TGF-β also induced PUMA in normal germinal center CD77-positive centroblasts isolated from human tonsil tissue. PUMA was a direct TGF-β target gene in B-cells, and we identify a putative Smad-binding region within the human PUMA promoter that recruits Smad3 and Smad4 in cells in response to TGF-β signaling. Constitutive activity of the isolated Smad-binding region in luciferase reporter assays was dependent on Smad consensus sequences and was partially dependent on endogenous TGF-β signaling and Smad4. Knockdown of PUMA in BL cells using lentiviral shRNA resulted in slower kinetics of the TGF-β-mediated apoptotic response. Analysis of Eμ-Myc cell lines demonstrated that c-myc-driven murine lymphomas are also sensitive to TGF-β-mediated apoptosis. Moreover, Puma(-/-) Eμ-Myc lines demonstrated significantly delayed kinetics of the apoptotic response when compared with wild type lymphomas. TGF-β therefore induces a polygenic response in Myc-driven lymphomas involving transcription of PUMA, which is necessary for the rapid induction of cell death.
Figures
References
-
- Li M. O., Wan Y. Y., Sanjabi S., Robertson A. K., Flavell R. A. (2006) Transforming growth factor-β regulation of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 24, 99–146 - PubMed
-
- Inman G. J., Allday M. J. (2000) Apoptosis induced by TGF-β1 in Burkitt's lymphoma cells is caspase 8 dependent but is death receptor independent. J. Immunol. 165, 2500–2510 - PubMed
-
- Shi Y., Massagué J. (2003) Mechanisms of TGF-β signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell 113, 685–700 - PubMed
-
- Derynck R., Zhang Y. E. (2003) Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-β family signalling. Nature 425, 577–584 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

