Lower frequency of obstructive sleep apnea in spondyloarthritis patients taking TNF-inhibitors
- PMID: 23243397
- PMCID: PMC3501660
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.2254
Lower frequency of obstructive sleep apnea in spondyloarthritis patients taking TNF-inhibitors
Abstract
Study objectives: Sleep disturbances, including obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), commonly limit function and quality of life in people with spondyloarthritis (SpA). Systemic inflammation has been implicated in the pathophysiology of both OSA and SpA, and suppression of inflammation with tumor necrosis factor α (TNF) inhibitors may decrease OSA severity. In this study, we compared the frequency of OSA in patients receiving and not receiving TNF-inhibitor therapy.
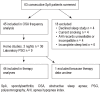
Methods: Data were collected from 63 consecutively screened veterans with SpA. Participant interviews, examinations, chart reviews, and referrals to the Salt Lake City Veteran Affairs (SLCVA) Sleep Center were used to obtain demographic data, comorbidities, SpA features, therapy data, and sleep study outcomes.
Results: OSA occurred in 76% of SpA patients. OSA was less common in patients receiving TNF-inhibitor therapy (57%), compared to patients not receiving TNF-inhibitor therapy (91%) (p = 0.01).
Conclusions: OSA is underrecognized in veterans with SpA, and TNF-inhibition was associated with a lower frequency of OSA.
Figures
Comment in
-
Obstructive sleep apnea and autoimmune disease: a two-way process.J Clin Sleep Med. 2013 Apr 15;9(4):409. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.2604. J Clin Sleep Med. 2013. PMID: 23585759 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Deodhar A, Braun J, Inman RD, et al. Golimumab reduces sleep disturbance in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis: results from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2010;62:1266–71. - PubMed
-
- Heiberg T, Lie E, van der Heijde D, Kvien TK. Sleep problems are of higher priority for improvement for patients with ankylosing spondylitis than for patients with other inflammatory arthropathies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70:872–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical