Odyssey of a cancer nanoparticle: from injection site to site of action
- PMID: 23243460
- PMCID: PMC3519442
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nantod.2012.10.010
Odyssey of a cancer nanoparticle: from injection site to site of action
Abstract
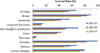
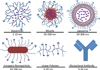
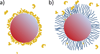
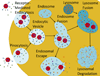
No chemotherapeutic drug can be effective until it is delivered to its target site. Nano-sized drug carriers are designed to transport therapeutic or diagnostic materials from the point of administration to the drug's site of action. This task requires the nanoparticle carrying the drug to complete a journey from the injection site to the site of action. The journey begins with the injection of the drug carrier into the bloodstream and continues through stages of circulation, extravasation, accumulation, distribution, endocytosis, endosomal escape, intracellular localization and-finally-action. Effective nanoparticle design should consider all of these stages to maximize drug delivery to the entire tumor and effectiveness of the treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Farber S, Diamond LK. New Engl. J. Med. 1948;238:787–793. - PubMed
-
- Viscomi S, Pastore G, Mosso ML, Teracini B, Madon E, Magnani C, et al. Haematol- Haematol J. 2003;88:974–982. - PubMed
-
- Mukherjee S. Emperor of All Maladies. New York, NY: Scribner; 2010.
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2012. Atlanta, GA: 2012.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
