Synthesis and SAR of 1-hydroxy-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-ones as Inhibitors of D-Amino Acid Oxidase
- PMID: 23243487
- PMCID: PMC3519437
- DOI: 10.1021/ml300212a
Synthesis and SAR of 1-hydroxy-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-ones as Inhibitors of D-Amino Acid Oxidase
Abstract
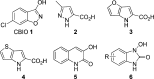
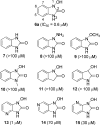
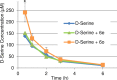
A series of 1-hydroxy-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2(3H)-ones were synthesized and evaluated for their ability to inhibit human and porcine forms of D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO). Inhibitory potency is largely dependent on the size and position of substituents on the benzene ring with IC(50) values of the compounds ranging from 70 nM to greater than 100 µM. Structure-activity relationships of this new class of DAAO inhibitors will be presented in detail along with comparisons to previously published SAR data from other classes of DAAO inhibitors. Some of these compounds were given to mice orally together with D-serine to assess their effects on plasma D-serine pharmacokinetics.
Figures

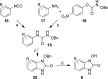
Similar articles
-
D-Amino acid oxidase inhibitors based on the 5-hydroxy-1,2,4-triazin-6(1H)-one scaffold.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016 Apr 15;26(8):2088-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.02.068. Epub 2016 Feb 23. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 26965861 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and initial SAR of 3-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)pyridin-2(1H)-ones as inhibitors of insulin-like growth factor 1-receptor (IGF-1R).Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Apr 15;17(8):2317-21. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.01.102. Epub 2007 Feb 4. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007. PMID: 17317169
-
Discovery of isatin and 1H-indazol-3-ol derivatives as d-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2018 May 1;26(8):1579-1587. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2018.02.004. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Bioorg Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29472125
-
Drug discovery strategies and the preclinical development of D-amino-acid oxidase inhibitors as antipsychotic therapies.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2018 Oct;13(10):973-982. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2018.1524459. Epub 2018 Sep 22. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 30220232 Review.
-
D-amino acid oxidase inhibitors as a novel class of drugs for schizophrenia therapy.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(14):2499-511. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319140002. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23116391 Review.
Cited by
-
6-Hydroxy-1,2,4-triazine-3,5(2H,4H)-dione Derivatives as Novel D-Amino Acid Oxidase Inhibitors.J Med Chem. 2015 Sep 24;58(18):7258-72. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00482. Epub 2015 Sep 3. J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26309148 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of kojic acid derivatives as secondary binding site probes of D-amino acid oxidase.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013 Jul 1;23(13):3910-3. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.04.062. Epub 2013 May 1. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2013. PMID: 23683589 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of 1-isopropyl-3-acyl-5-methyl-benzimidazolone derivatives and their antimicrobial activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Mar 26;14(4):6790-804. doi: 10.3390/ijms14046790. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23531538 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of tautomeric and protomeric binding modes by free energy calculations. A case study for the structure based optimization of D-amino acid oxidase inhibitors.J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2018 Feb;32(2):331-345. doi: 10.1007/s10822-018-0097-y. Epub 2018 Jan 15. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 2018. PMID: 29335871
-
Bioactive heterocycles containing endocyclic N-hydroxy groups.Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Jun 5;97:505-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.11.031. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25466924 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Javitt D. C. Glutamatergic theories of schizophrenia. Isr. J Psychiatry Relat. Sci. 2010, 47, 4–16. - PubMed
-
- Oldendorf W. H. Brain uptake of radiolabeled amino acids, amines, and hexoses after arterial injection. Am. J. Physiol. 1971, 221, 1629–1639. - PubMed
-
- Williams R. E.; Lock E. A. Sodium benzoate attenuates D-serine induced nephrotoxicity in the rat. Toxicology 2005, 207, 35–48. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

