An Association between Bevacizumab and Recurrent Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient Presenting with Deep Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- PMID: 23243534
- PMCID: PMC3517831
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/819546
An Association between Bevacizumab and Recurrent Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome in a Patient Presenting with Deep Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
Background. The posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a syndrome characterized by hypertension, headache, seizures, and visual disturbances. Causes of PRES include preeclampsia/eclampsia, hypertension, and recently bevacizumab, a monoclonal antibody vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) inhibitor. There is no information to date about PRES recurrence in patients taking bevacizumab or descriptions of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the setting of PRES. We reviewed data on a patient receiving bevacizumab who presented with a DVT and PRES and later developed recurrent PRES. Case. A 72-year-old man with metastatic pulmonary adenocarcinoma received maintenance bevacizumab following six cycles of carboplatin and paclitaxel. Following his eighth dose of bevacizumab, he developed a DVT as well as PRES. He made a rapid recovery and was discharged from the hospital but went on to develop PRES recurrence nine days following his original episode. Conclusion. Several mechanisms exist whereby exposure to bevacizumab could be related to the development of both DVT and PRES by inducing global endothelial dysfunction. Recurrent PRES may result from bevacizumab's prolonged half-life (11-50 days) and suboptimal blood pressure control. In the setting of bevacizumab, PRES surveillance may play a similar role in preeclampsia screening as both diseases share similar antiangiogenic signaling pathways.
Figures
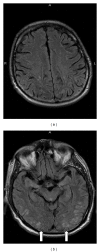
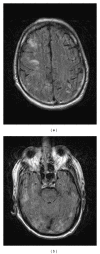
References
-
- Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1996;334(8):494–500. - PubMed
-
- Glusker P, Recht L, Lane B. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome and bevacizumab. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2006;354:980–982. - PubMed
-
- Sweany JM, Bartynski WS, Boardman JF. ‘Recurrent’ posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: report of 3 cases—PRES can strike twice! Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography. 2007;31(1):148–156. - PubMed
-
- Lau PCP, Paunipagar B. Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome with bevacizumab. Hong Kong Medical Journal. 2011;17(1):80–81. - PubMed
-
- Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, et al. Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2006;355(24):2542–2550. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

