Accelerating mesh-based Monte Carlo method on modern CPU architectures
- PMID: 23243572
- PMCID: PMC3521306
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.3.003223
Accelerating mesh-based Monte Carlo method on modern CPU architectures
Abstract
In this report, we discuss the use of contemporary ray-tracing techniques to accelerate 3D mesh-based Monte Carlo photon transport simulations. Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) based computation and branch-less design are exploited to accelerate ray-tetrahedron intersection tests and yield a 2-fold speed-up for ray-tracing calculations on a multi-core CPU. As part of this work, we have also studied SIMD-accelerated random number generators and math functions. The combination of these techniques achieved an overall improvement of 22% in simulation speed as compared to using a non-SIMD implementation. We applied this new method to analyze a complex numerical phantom and both the phantom data and the improved code are available as open-source software at http://mcx.sourceforge.net/mmc/.
Keywords: (170.3660) Light propagation in tissues; (170.5280) Photon migration; (170.7050) Turbid media.
Figures
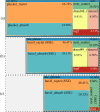
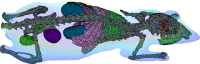
References
-
- Boas D. A., Brooks D. H., Miller E. L., DiMarzio C. A., Kilmer M., Gaudette R. J., Zhang Q., “Imaging the body with diffuse optical tomography,” IEEE Signal Proc. Mag. 18, 57–75 (2001).10.1109/79.962278 - DOI
-
- Boas D. A., Culver J., Stott J., Dunn A., “Three dimensional Monte Carlo code for photon migration through complex heterogeneous media including the adult human head,” Opt. Express 10, 159–170 (2002). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
