Event-related potentials for 7-month-olds' processing of animals and furniture items
- PMID: 23245220
- PMCID: PMC6987642
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dcn.2012.09.002
Event-related potentials for 7-month-olds' processing of animals and furniture items
Abstract
Event-related potentials (ERPs) to single visual stimuli were recorded in 7-month-old infants. In a three-stimulus oddball paradigm, infants watched one frequently occurring standard stimulus (either an animal or a furniture item) and two infrequently occurring oddball stimuli, presenting one exemplar from the same and one from the different superordinate category as compared to the standard stimulus. Additionally, visual attributes of the stimuli were controlled to investigate whether infants focus on category membership or on perceptual similarity when processing the stimuli. Infant ERPs indicated encoding of the standard stimulus and discriminating it from the two oddball stimuli by larger Nc peak amplitude and late-slow-wave activity for the infrequent stimuli. Moreover, larger Nc latency and positive-slow-wave activity indicated increased processing for the different-category as compared to the same-category oddball. Thus, 7-month-olds seem to encode single stimuli not only by surface perceptual features, but they also regard information of category membership, leading to facilitated processing of the oddball that belongs to the same domain as the standard stimulus.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

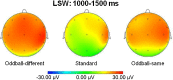
Similar articles
-
Three-month-olds' brain responses to upright and inverted faces and cars.Dev Neuropsychol. 2013;38(4):272-80. doi: 10.1080/87565641.2013.786719. Dev Neuropsychol. 2013. PMID: 23682666
-
Event-related potentials of 4-7-week-old infants in a visual recognition memory task.Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1995 Jun;94(6):414-24. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(94)00313-a. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1995. PMID: 7607095
-
Auditory processing in an inter-modal oddball task: effects of a combined auditory/visual standard on auditory target ERPs.Int J Psychophysiol. 2007 Aug;65(2):122-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2007.04.002. Epub 2007 Apr 11. Int J Psychophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17481761
-
Do animals and furniture items elicit different brain responses in human infants?Brain Dev. 2010 Nov;32(10):863-71. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2009.11.010. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Brain Dev. 2010. PMID: 20022721
-
Attention or memory? Effects of familiarity and novelty on the Nc component of event-related brain potentials in six-month-old infants.Int J Neurosci. 2007 Jun;117(6):837-67. doi: 10.1080/00207450600909970. Int J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17454247
Cited by
-
Development, Insults and Predisposing Factors of the Brain's Predictive Coding System to Chronic Perceptual Disorders-A Life-Course Examination.Brain Sci. 2024 Jan 16;14(1):86. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14010086. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38248301 Free PMC article.
-
Visual segmentation of complex naturalistic structures in an infant eye-tracking search task.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 1;17(4):e0266158. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266158. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35363809 Free PMC article.
-
Nine-month-old infants update their predictive models of a changing environment.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2019 Aug;38:100680. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2019.100680. Epub 2019 Jul 10. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31357079 Free PMC article.
-
What do infants understand of others' action? A theoretical account of early social cognition.Psychol Res. 2014 Sep;78(5):609-22. doi: 10.1007/s00426-013-0519-3. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Psychol Res. 2014. PMID: 24100453 Review.
-
The Development of Global-Level Categorization: Frequency Tagging EEG Responses.Brain Sci. 2024 May 24;14(6):541. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14060541. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ackles P., Cook K. Stimulus probability and event-related potentials of the brain in 6-month-old human infants. A parametric study. International Journal of Psychophysiology. 1998;29:115–143. - PubMed
-
- Courchesne E., Ganz L., Norcia A.M. Event-related brain potentials to human faces in infants. Child Development. 1981;52:804–811. - PubMed
-
- de Haan M. Psychology Press; New York: 2007. Infant EEG and Event-related Potentials.
-
- de Haan M., Nelson C.A. Recognition of the mother's face by six-month-old infants. Child Development. 1997;68:187–210. - PubMed
-
- Gelman S.A., Opfer J.E. Development of the animate–inanimate distinction. In: Goswami U., editor. Blackwell Handbook of Childhood Cognitive Development. Blackwell Publishing; Malden: 2002. pp. 151–166.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

