L-asparaginase II produced by Salmonella typhimurium inhibits T cell responses and mediates virulence
- PMID: 23245323
- PMCID: PMC4361029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.10.018
L-asparaginase II produced by Salmonella typhimurium inhibits T cell responses and mediates virulence
Abstract
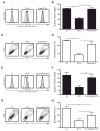
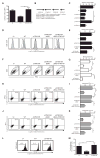
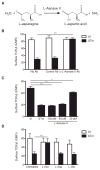
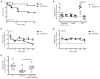
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium avoids clearance by the host immune system by suppressing T cell responses; however, the mechanisms that mediate this immunosuppression remain unknown. We show that S. Typhimurium inhibit T cell responses by producing L-Asparaginase II, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of L-asparagine to aspartic acid and ammonia. L-Asparaginase II is necessary and sufficient to suppress T cell blastogenesis, cytokine production, and proliferation and to downmodulate expression of the T cell receptor. Furthermore, S. Typhimurium-induced inhibition of T cells in vitro is prevented upon addition of L-asparagine. S. Typhimurium lacking the L-Asparaginase II gene (STM3106) are unable to inhibit T cell responses and exhibit attenuated virulence in vivo. L-Asparaginases are used to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia through mechanisms that likely involve amino acid starvation of leukemic cells, and these findings indicate that pathogens similarly use L-asparagine deprivation to limit T cell responses.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contribution of Asparagine Catabolism to Salmonella Virulence.Infect Immun. 2017 Jan 26;85(2):e00740-16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00740-16. Print 2017 Feb. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 27849183 Free PMC article.
-
Asparagine deprivation mediated by Salmonella asparaginase causes suppression of activation-induced T cell metabolic reprogramming.J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Feb;99(2):387-98. doi: 10.1189/jlb.4A0615-252R. Epub 2015 Oct 23. J Leukoc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26497246 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and pathophysiological characterization of Helicobacter pylori asparaginase.Microbiol Immunol. 2011 Jun;55(6):408-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.2011.00333.x. Microbiol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21395663
-
Recent research progress on microbial L-asparaginases.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Feb;99(3):1069-79. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-6271-9. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25492420 Review.
-
Mechanisms used by virulent Salmonella to impair dendritic cell function and evade adaptive immunity.Immunology. 2012 Sep;137(1):28-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2012.03614.x. Immunology. 2012. PMID: 22703384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic analysis of antimicrobial effects of pegylated silver coated carbon nanotubes in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.J Nanobiotechnology. 2018 Mar 27;16(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0355-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018. PMID: 29587743 Free PMC article.
-
Direct visualization of endogenous Salmonella-specific B cells reveals a marked delay in clonal expansion and germinal center development.Eur J Immunol. 2015 Feb;45(2):428-41. doi: 10.1002/eji.201444540. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25346524 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the bio-catalysis scope and applied perspectives of nanocarrier immobilized asparaginases.3 Biotech. 2021 Oct;11(10):453. doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-02999-y. Epub 2021 Oct 1. 3 Biotech. 2021. PMID: 34616647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycoplasma genitalium Protein of Adhesion Suppresses T Cell Activation via CypA-CaN-NFAT Pathway.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0450322. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04503-22. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37074201 Free PMC article.
-
Eucalyptol, sabinene and cinnamaldehyde: potent inhibitors of salmonella target protein L-asparaginase.3 Biotech. 2017 Aug;7(4):258. doi: 10.1007/s13205-017-0891-6. Epub 2017 Jul 22. 3 Biotech. 2017. PMID: 28735432 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI007539/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI083646/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057158/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21AI083964/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56AI077645/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI075093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007964/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI101221/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI092165/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32AI007539/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM007964/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK034854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI055621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI075093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01AI055621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI083646/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI083964/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI077645/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

