The Yersinia virulence effector YopM binds caspase-1 to arrest inflammasome assembly and processing
- PMID: 23245324
- PMCID: PMC3703949
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.10.020
The Yersinia virulence effector YopM binds caspase-1 to arrest inflammasome assembly and processing
Abstract
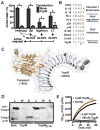
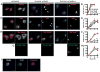
Inflammasome assembly activates caspase-1 and initiates the inflammatory cell death program pyroptosis, which is protective against numerous pathogens. Consequently, several pathogens, including the plague causing bacterium Yersinia pestis, avoid activating this pathway to enhance their virulence. However, bacterial molecules that directly modulate the inflammasome have yet to be identified. Examining the contribution of Yersinia type III secretion effectors to caspase-1 activation, we identified the leucine-rich repeat effector YopM as a potent antagonist of both caspase-1 activity and activation. YopM directly binds caspase-1, which both inhibits caspase-1 activity and sequesters it to block formation of the mature inflammasome. Caspase-1 activation antagonizes Yersinia survival in vivo, and consequently YopM inhibition of caspase-1 is required for Yersinia pathogenesis. Thus, a bacterium obstructs pyroptosis utilizing a direct mechanism of caspase-1 inhibition that is distinct from known viral or host inhibitors.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
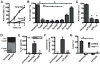
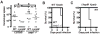
Comment in
-
YopM puts caspase-1 on ice.Cell Host Microbe. 2012 Dec 13;12(6):737-8. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.11.006. Cell Host Microbe. 2012. PMID: 23245318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bauernfeind FG, Horvath G, Stutz A, Alnemri ES, MacDonald K, Speert D, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, Monks BG, Fitzgerald KA, et al. Cutting Edge: NF-kB Activating Pattern Recognition and Cytokine Receptors License NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Regulating NLRP3 Expression. J Immunol. 2009;183:787–791. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

