Hypopulvins, novel peptaibiotics from the polyporicolous fungus Hypocrea pulvinata, are produced during infection of its natural hosts
- PMID: 23245616
- PMCID: PMC4886835
- DOI: 10.1016/j.funbio.2012.10.003
Hypopulvins, novel peptaibiotics from the polyporicolous fungus Hypocrea pulvinata, are produced during infection of its natural hosts
Abstract
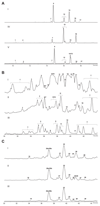
In order to investigate the significance of antibiotics for the producing organism(s) in the natural habitat, we screened specimens of the polyporicolous fungus Hypocrea pulvinata growing on its natural hosts Piptoporus betulinus and Fomitopsis pinicola. Results showed that a particular group of nonribosomally biosynthesised antibiotic polypeptides, the peptaibiotics, which contain the nonproteinogenic marker amino acid α-aminoisobutyric acid (Aib), was produced in the natural habitat by the fungicolous producer and, consequently, released into the host. Using liquid chromatography coupled to electrospray high-resolution mass spectrometry we detected especially 19-, but also 11-, 18-, and 20-residue peptaibiotics in the five infected specimens analysed. Structures of peptaibiotics found were confirmed by analysing the peptaibiome of pure agar cultures obtained by single-ascospore isolation from the specimens. The 19-residue peptaibols were determined as deletion sequences of the trichosporins B lacking the Aib residue in position 6. Notably, 26 of the 28 peptaibiotics sequenced were novel; therefore the name 'hypopulvins' was introduced. Considering not only the ubiquity of both the two host species but also the highly specific association between H. pulvinata and P. betulinus/F. pinicola, and the abundance of this fungicolous species in north temperate regions of the world, a decisive role for the peptaibiotics detected in this study is predicted, which may act as mediators of the complex interactions between the basidiomycetous host and its fungicolous ascomycete 'partner'. Structural analogies of the hypopulvins, particularly with other 18-, 19-, and 20-residue peptaibiotics, suggest that the hypopulvins are forming transmembrane ion channels and could thus support the hypothesis of a parasitic lifestyle of the fungicolous producer.
Copyright © 2012 The British Mycological Society. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Front line defenders of the ecological niche! Screening the structural diversity of peptaibiotics from saprotrophic and fungicolous Trichoderma/Hypocrea species.Fungal Divers. 2014 Nov 1;69(1):117-146. doi: 10.1007/s13225-013-0276-z. Fungal Divers. 2014. PMID: 25722662 Free PMC article.
-
Screening the biosphere: the fungicolous fungus Trichoderma phellinicola, a prolific source of hypophellins, new 17-, 18-, 19-, and 20-residue peptaibiotics.Chem Biodivers. 2013 May;10(5):787-812. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201200339. Chem Biodivers. 2013. PMID: 23681726 Free PMC article.
-
Peptaibiomics: an advanced, rapid and selective analysis of peptaibiotics/peptaibols by SPE/LC-ES-MS.Amino Acids. 2006 Jun;30(4):435-43. doi: 10.1007/s00726-005-0275-9. Epub 2006 Apr 20. Amino Acids. 2006. PMID: 16622603
-
Recent advances and future prospects in peptaibiotics, hydrophobin, and mycotoxin research, and their importance for chemotaxonomy of Trichoderma and Hypocrea.Chem Biodivers. 2008 May;5(5):671-80. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200890064. Chem Biodivers. 2008. PMID: 18493954 Review.
-
Peptaibiomics: towards a myriad of bioactive peptides containing C(alpha)-dialkylamino acids?Chem Biodivers. 2008 Sep;5(9):1817-43. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200890171. Chem Biodivers. 2008. PMID: 18816513 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Expression of Genes Involved in Host Recognition, Attachment, and Degradation in the Mycoparasite Tolypocladium ophioglossoides.G3 (Bethesda). 2016 Jan 22;6(3):731-41. doi: 10.1534/g3.116.027045. G3 (Bethesda). 2016. PMID: 26801645 Free PMC article.
-
New 19-Residue Peptaibols from Trichoderma Clade Viride.Microorganisms. 2018 Aug 12;6(3):85. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms6030085. Microorganisms. 2018. PMID: 30103563 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Diversity and Bioactivities of Peptaibol Compounds From the Longibrachiatum Clade of the Filamentous Fungal Genus Trichoderma.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jun 26;10:1434. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01434. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31293557 Free PMC article.
-
Trachymyrmex septentrionalis ants promote fungus garden hygiene using Trichoderma-derived metabolite cues.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Jun 20;120(25):e2219373120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2219373120. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 37319116 Free PMC article.
-
Front line defenders of the ecological niche! Screening the structural diversity of peptaibiotics from saprotrophic and fungicolous Trichoderma/Hypocrea species.Fungal Divers. 2014 Nov 1;69(1):117-146. doi: 10.1007/s13225-013-0276-z. Fungal Divers. 2014. PMID: 25722662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anonymous, Novembro 2011/Fevereiro. Ministério da agricultura, pecuária e abastecimento (Mapa)/comissão executiva do plano da lavoura cacaueira (Ceplac). Ministério da agricultura aprovou registro do tricovab para combate à vassoura-de-bruxa. Jornal de Cacau. 2012;6:5.
-
- Becker D, Kiess M, Brückner H. Structures of peptaibol antibiotics hypomurocin A and B from the ascomycetous fungus Hypocrea muroiana Hino et Katsumoto. Liebigs Annalen Recueil. 1997:767–772.
-
- Bérdy J. Thoughts and facts about antibiotics: where we are now and where we are heading. Journal of Antibiotics 65: 385–395 Corrigendum. Journal of Antibiotics. 2012;65:441. - PubMed
-
- Berek I, Becker A, Schröder H, Härtl A, Höllt V, Grecksch G. Ampullosporin A, a peptaibol from Sepedonium ampullosporum HKI-0053 with neuroleptic-like activity. Behavioural Brain Research. 2009;203:232–239. - PubMed
-
- Berg A, Grigoriev PA, Degenkolb T, Neuhof T, Härtl A, Schlegel B, Gräfe U. Isolation, structure elucidation and biological activities of trichofumins A, B, C and D, new 11 and 13mer peptaibols from Trichoderma sp. HKI 0276. Journal of Peptide Science. 2003;9:810–816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

