Embryonic stem cell and induced pluripotent stem cell: an epigenetic perspective
- PMID: 23247625
- PMCID: PMC3541668
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2012.175
Embryonic stem cell and induced pluripotent stem cell: an epigenetic perspective
Abstract
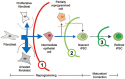
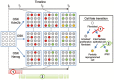
Pluripotent stem cells, like embryonic stem cells (ESCs), have specialized epigenetic landscapes, which are important for pluripotency maintenance. Transcription factor-mediated generation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) requires global change of somatic cell epigenetic status into an ESC-like state. Accumulating evidence indicates that epigenetic mechanisms not only play important roles in the iPSC generation process, but also affect the properties of reprogrammed iPSCs. Understanding the roles of various epigenetic factors in iPSC generation contributes to our knowledge of the reprogramming mechanisms.
Figures
References
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

