Mimics in chest disease: interstitial opacities
- PMID: 23247773
- PMCID: PMC3579994
- DOI: 10.1007/s13244-012-0207-7
Mimics in chest disease: interstitial opacities
Abstract
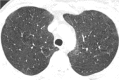
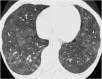
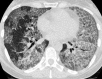
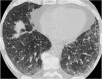
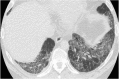
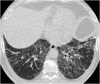
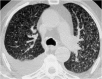
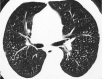
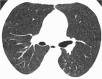
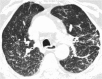
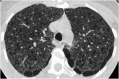
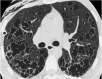
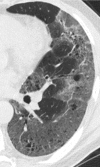
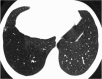
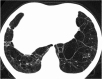
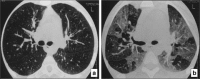
Septal, reticular, nodular, reticulonodular, ground-glass, crazy paving, cystic, ground-glass with reticular, cystic with ground-glass, decreased and mosaic attenuation pattern characterise interstitial lung diseases on high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT). Occasionally different entities mimic each other, either because they share identical HRCT findings or because of superimposition of patterns. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), fibrosis associated with connective tissue disease, asbestosis, end-stage sarcoidosis or chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) may present with lower zone, subpleural reticular pattern associated with honeycombing. Lymphangiomyomatosis may be indistinguishable from histiocytosis or extensive emphysema. Both pulmonary oedema and lymphangitic carcinomatosis may be characterised by septal pattern resulting from thickened interlobular septa. Ill-defined centrilobular nodular pattern may be identically present in HP and respiratory bronchiolitis-associated with interstitial lung disease (RBILD). Sarcoidosis may mimic miliary tuberculosis or haematogenous metastases presenting with miliary pattern, while endobronchial spread of tuberculosis may be indistinguishable from panbronchiolitis, both presenting with tree-in-bud pattern. Atypical infection presenting with ground-glass mimics haemorrhage. Ground-glass pattern with minimal reticulation is seen in desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP), RBILD and non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP). Obliterative bronchiolitis and panlobular emphysema may present with decreased attenuation pattern, while obliterative bronchiolitis, chronic pulmonary embolism and HP may manifest with mosaic attenuation pattern. Various mimics in interstitial lung diseases exist. Differential diagnosis is narrowed based on integration of predominant HRCT pattern and clinical history. Teaching Points • To learn about the different HRCT patterns, which are related to interstitial lung diseases. • To be familiar with the more "classical" entities presenting with each HRCT pattern. • To discuss possible overlap of different HRCT patterns and the more common mimics in each case. • To learn about some clues that help differentiate the various diagnostic mimics on HRCT.
Figures
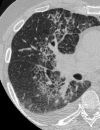
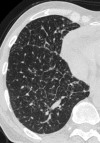
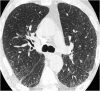
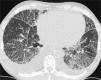
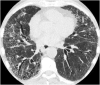
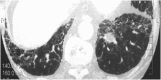
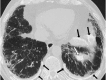
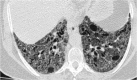
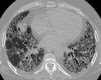
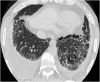
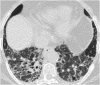
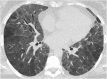
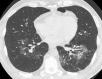
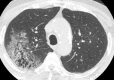
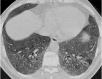
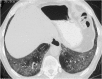
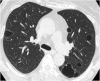
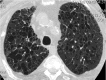
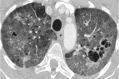
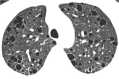
Similar articles
-
A comparative study of honeycombing on high resolution computed tomography with histologic lung remodeling in explants with usual interstitial pneumonia.Pathol Res Pract. 2015 Jan;211(1):55-61. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2014.08.013. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Pathol Res Pract. 2015. PMID: 25433993
-
Clinical and radiological features of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIPs): a pictorial review.Insights Imaging. 2014 Jun;5(3):347-64. doi: 10.1007/s13244-014-0335-3. Epub 2014 May 22. Insights Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24844883 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: Is the emphysema type associated with the pattern of fibrosis?World J Radiol. 2015 Sep 28;7(9):294-305. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i9.294. World J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 26435780 Free PMC article.
-
The idiopathic interstitial pneumonias.Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2004 Sep-Oct;33(5):189-99. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2004.04.003. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2004. PMID: 15459629 Review.
-
CT signs and patterns of lung disease.Radiol Clin North Am. 2001 Nov;39(6):1115-35. doi: 10.1016/s0033-8389(05)70334-1. Radiol Clin North Am. 2001. PMID: 11699664 Review.
Cited by
-
The radiologist's role in detecting systemic anticancer therapy-related interstitial lung disease: an educational review.Insights Imaging. 2024 Aug 1;15(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s13244-024-01771-z. Insights Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39090512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis using medical imaging techniques and artificial intelligence: A review.Clin Imaging. 2021 Aug;76:6-14. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.01.019. Epub 2021 Jan 28. Clin Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33545517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of morphological characteristics assessed by CT scan in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Dec;11(12):3521-3527. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13695. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33044045 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of 12-zone lung ultrasound protocol for diagnosing COVID-19-associated pneumonia in outpatients.J Ultrason. 2021 Nov 29;21(87):e271-e276. doi: 10.15557/JoU.2021.0046. Epub 2021 Dec 15. J Ultrason. 2021. PMID: 34970436 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: do not miss the chance for an early diagnosis.Am J Case Rep. 2014 Sep 5;15:378-81. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.891014. Am J Case Rep. 2014. PMID: 25203436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glaspole IN, du Bois RM, Wells AU. The application of high-resolution CT to diagnosis in diffuse parenchymal lung disease. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis. 2001;56:233–239. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

