Diabetes and risk of fracture-related hospitalization: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study
- PMID: 23248194
- PMCID: PMC3631877
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-1168
Diabetes and risk of fracture-related hospitalization: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study
Abstract
Objective: To examine the association between diabetes, glycemic control, and risk of fracture-related hospitalization in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study.
Research design and methods: Fracture-related hospitalization was defined using International Classification of Diseases, 9th revision, codes (733.1-733.19, 733.93-733.98, or 800-829). We calculated the incidence rate of fracture-related hospitalization by age and used Cox proportional hazards models to investigate the association of diabetes with risk of fracture after adjustment for demographic, lifestyle, and behavioral risk factors.
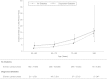
Results: There were 1,078 incident fracture-related hospitalizations among 15,140 participants during a median of 20 years of follow-up. The overall incidence rate was 4.0 per 1,000 person-years (95% confidence interval [CI], 3.8-4.3). Diagnosed diabetes was significantly and independently associated with an increased risk of fracture (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 1.74; 95% CI, 1.42-2.14). There also was a significantly increased risk of fracture among persons with diagnosed diabetes who were treated with insulin (HR, 1.87; 95% CI, 1.15-3.05) and among persons with diagnosed diabetes with hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) ≥8% (1.63; 1.09-2.44) compared with those with HbA1c <8%. Undiagnosed diabetes was not significantly associated with risk of fracture (HR, 1.12; 95% CI, 0.82-1.53).
Conclusions: This study supports recommendations from the American Diabetes Association for assessment of fracture risk and implementation of prevention strategies in persons with type 2 diabetes, particularly those persons with poor glucose control.
Figures
References
-
- Prieto-Alhambra D, Aviles FF, Judge A, Van Staa T, Nogues X, Arden NK, et al. Burden of pelvis fracture: a population-based study of incidence, hospitalisation and mortality. Osteoporos Int 2012;23:2797–2803 - PubMed
-
- Hepgüler S, Cetin A, Değer C, Erkent U. Osteoporotic hip fracture costs in the elderly Turkish population. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 2011;45:316–325 - PubMed
-
- Schwartz AV, Vittinghoff E, Bauer DC, et al. Study of Osteoporotic Fractures (SOF) Research Group. Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Research Group. Health, Aging, and Body Composition (Health ABC) Research Group Association of BMD and FRAX score with risk of fracture in older adults with type 2 diabetes. JAMA 2011;305:2184–2192 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Janghorbani M, Van Dam RM, Willett WC, Hu FB. Systematic review of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of fracture. Am J Epidemiol 2007;166:495–505 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089174/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK076595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK062707/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK080294/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

