Efficacy of a parent-youth teamwork intervention to promote adherence in pediatric asthma
- PMID: 23248342
- PMCID: PMC3701124
- DOI: 10.1093/jpepsy/jss123
Efficacy of a parent-youth teamwork intervention to promote adherence in pediatric asthma
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether a parent-youth teamwork intervention improved medication adherence and related outcomes among youth with asthma.
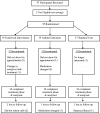
Methods: We used a randomized clinical trial with 48 youth (aged 9-15 years) assigned to 1 of 3 groups: Teamwork Intervention (TI), Asthma Education (AE), or Standard Care (SC). Treatment occurred across 2 months, with a 3-month follow-up assessment. Adherence to inhaled corticosteroids was assessed via the MDILog-II. Parent-adolescent conflict, asthma functional severity, and spirometry assessments were obtained pre-treatment, post-treatment, and on follow-up. Mixed linear model analysis was used to evaluate group and time effects for outcome measures.
Results: TI group had significantly higher adherence and lower functional severity scores than AE or SC conditions, and lower parent-reported conflict and a trend for higher spirometry values compared with the SC group.
Conclusions: Results suggest support for the efficacy of TI for improving medication adherence as youth acquire more responsibility for their asthma management.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00166582.
Keywords: adherence; asthma education; electronic monitoring; parent–youth teamwork; pediatric asthma.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson B, Brackett J, Ho J, Laffel L M. An office-based intervention to maintain parent-adolescent teamwork in diabetes management. Impact on parent involvement, family conflict, and subsequent glycemic control. Diabetes Care. 1999;22:713–721. - PubMed
-
- Apter A J, Tor M, Feldman H I. Testing the reliability of old and new features of a new electronic monitor for metered dose inhalers. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology. 2001;86:421–424. - PubMed
-
- Bartlett S J, Lukk P, Butz A, Lampros-Klein F, Rand C S. Enhancing medication adherence among inner-city children with asthma: Results from pilot studies. Journal of Asthma. 2002;39:47–54. - PubMed
-
- Bender B, Bartlett S, Rand C, Turner C, Wamboldt F, Zhang L. Impact of interview mode on accuracy of child and parent report of adherence with asthma-controller medication. Pediatrics. 2007;120:e471–e470. - PubMed
-
- Bender B, Bender S. Patient-identified barriers to asthma treatment adherence: Response to interviews, focus groups, and questionnaires. Immunology and Allergy Clinics of North America. 2005;25:107–130. - PubMed