Verruciform xanthoma: report of five cases
- PMID: 23248367
- PMCID: PMC3519256
- DOI: 10.4103/0019-5154.103069
Verruciform xanthoma: report of five cases
Abstract
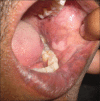
We describe five cases of verruciform xanthoma (VX). The patients, all males, presented with single warty verrucous lesions of 0.5-2 cm size that had been diagnosed clinically as viral warts (four cases) and leukoplakia (one case). Two patients had the lesion in the oral cavity, two on the genital mucosa, and one on the scrotal skin. Histopathology was diagnostic, with verrucous and papillomatous epidermal hyperplasia with the silhouette of a viral wart but with numerous foamy histiocytes packed in the elongated dermal papillae. Columns of deep parakeratosis and neutrophils in the upper spinous layers, with a dermal plasma cell infiltrate were the other histopathologic findings. Excision of the lesions was curative, without recurrences, in the two patients who had lesions in the oral cavity; follow-up was not available in the cases with genital lesions. VX is an uncommon but distinctive clinicopathologic entity affecting the oral and genital mucosa that may be mistaken for benign, premalignant, and malignant conditions. VX can be diagnosed with certainty only on histopathologic examination.
Keywords: Foam cells; verruciform xanthoma; viral wart.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Shafer W. Verruciform xanthoma. Oral Surg. 1971;31:784–9. - PubMed
-
- Buchner A, Hansen LS, Merell PW. Verruciform xanthoma of the oral mucosa. Report of five cases and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 1981;117:563–5. - PubMed
-
- Nowparast B, Howell FV, Rick GM. Verruciform xanthoma. A clinico-pathologic review and report of fifty four cases. Oral Surg. 1981;51:619–25. - PubMed
-
- Santa Cruz DJ, Martin SA. Verruciform xanthoma of the vulva. Report of two cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979;71:224–8. - PubMed
-
- Al-Nafussi AI, Azzopardi JG, Salm R. Verruciform xanthoma of skin. Histopathology. 1985;9:245–52. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
