Epidermoid cyst of submandibular region
- PMID: 23248482
- PMCID: PMC3519225
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-029X.102511
Epidermoid cyst of submandibular region
Abstract
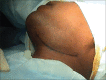
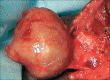
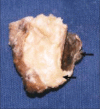
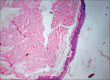
Epidermoid cysts are rare, slow-growing, benign, developmental cysts that are derived from abnormally situated ectodermal tissue. Epidermoid cysts may grow anywhere on the body and about 7% of them are located in the head and neck. These cyst arise from traumatic implantation of epithelium or entrapment of epithelial remnants during embryonic fusion. Histopathologically, they are lined by stratified squamous epithelium and ,lumen without any skin appendages. Here we present a case of epidermod cyst occurring in sub-mandibular region.
Keywords: Dermoid cyst; epidermoid cyst; skin appendages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Shafer WG, Hine MK, Levy BM. 4th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1993. A text book of Oral Pathology.
-
- Koca H, Seckin T, Sipahi A, Kaznac A. Epidermoid cyst in the floor of the mouth: Report of a case. Quintessence Int. 2007;38:473–7. - PubMed
-
- Ozan F, Polat HB, Ay S, Goze F. Epidermoid cyst of the buccal mucosa: A case report. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2007;3:90–6. - PubMed
-
- Pancholi A, Raniga S, Vohra PA, Vaidya V. Midline submental epidermoid cyst: A Rare Case. Internet J Otorhinolaryngol. 2006;2

