Squash(ed): Craniofacial and vertebral injury from collision on squash court
- PMID: 23248511
- PMCID: PMC3519055
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-2700.102415
Squash(ed): Craniofacial and vertebral injury from collision on squash court
Abstract
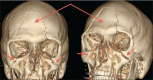
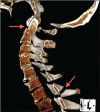
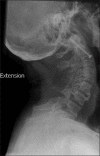
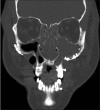
Squash is a popular racquet sport not usually associated with severe head or spinal injury. The incidence of squash-related injury ranges from 35.5 to 80.9 per 100,000 players, with the most common sites being the lower-limbs and eyes. We present a case of extensive traumatic craniomaxillofacial and vertebral injury resulting from collision on a squash court, without use of protective gear. The patient sustained fractures of the frontal bone, orbits, maxillae, zygomas, the first and second cervical vertebrae and the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertrebra. This is the first case of squash-related injury with such extensive craniofacial and vertebral involvement. This unique case required multiple surgical procedures as well as an extensive admission to the intensive care unit and highlights the risk of significant craniomaxillofacial trauma in sports not usually associated with such injuries.
Keywords: Athletic injuries; bone; craniocerebral trauma; fractures; spinal injuries.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Eime R, Zazryn T, Finch C. Epidemiology of squash injuries requiring hospital treatment. Inj Control Saf Promot. 2003;10:243–5. - PubMed
-
- Finch C, Eime R. The epidemiology of squash injuries. Int Sports Med J. 2001;2:1.
-
- Katzen JT, Jarrahy R, Eby JB, Mathiasen RA, Margulies DR, Shahinian HK. Craniofacial and skull base trauma. J Trauma. 2003;54:1026–34. - PubMed
-
- Jones DE, Evans JN. “Blow-out” fractures of the orbit: An investigation into their anatomical basis. J Laryngol Otol. 1967;81:1109–20. - PubMed
-
- Hwang K, You SH, Lee HS. Outcome analysis of sports-related multiple facial fractures. J Craniofac Surg. 2009;20:825–9. - PubMed

