Role of paclitaxel and platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy in high-risk penile cancer
- PMID: 23248520
- PMCID: PMC3519105
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-7796.102659
Role of paclitaxel and platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy in high-risk penile cancer
Abstract
Aim: To study the efficacy and safety of paclitaxel and platinum doublet chemotherapy in penile cancer patients with high-risk features of local failure.
Materials and methods: Retrospective analysis was done of patients with 19 carcinoma of the penis who were offered adjuvant chemotherapy with paclitaxel and platinum combination. The data regarding the surgical details, high-risk features for which chemotherapy was offered, chemotherapy toxicity details (in accordance with CTCAE vs 3), failure pattern, and survival data were noted. SPSS version 16 was used for statistical analysis. Descriptive and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was performed.
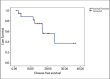
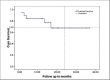
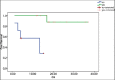
Results: Median age of patients was 48 years. Fifteen patients received paclitaxel in combination with cisplatin and four received paclitaxel with carboplatin in view of their low serum creatinine clearance. The treatment was completed by 12 patients (63.2%). Of 79 planned cycles, 50 were taken. The treatment was well tolerated with grade 3-4 gastrointestinal toxicity was seen in 1 patient, grade 3 neurological toxicity in one and grade 5 neutropenia in one patient. Treatment related death occured in one patient. The median follow-up was 15.33 months and 6 loco-regional relapsed had taken place. The estimated median DFS was 16.2 months and the estimated median OS was not reached. The estimated DFS for treatment completed patients was 23.13 months as against 2.16 months for patients not completing treatment.
Conclusion: The platinum and taxane doublet chemotherapy was found to be safe and effective.
Keywords: Adjuvant chemotherapy; carcinoma of the penis; platinum.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Palliative chemotherapy in carcinoma penis: Does platinum and taxane combination holds a promise?Urol Ann. 2014 Jan;6(1):18-22. doi: 10.4103/0974-7796.127011. Urol Ann. 2014. PMID: 24669116 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of metronomic administration of paclitaxel for advanced recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer.Indian J Cancer. 2013 Apr-Jun;50(2):122-7. doi: 10.4103/0019-509X.117032. Indian J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23979203
-
Platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy on moderate- and high-risk stage I and II epithelian ovarian cancer patients. Long-term single institution experience and literature review.Clin Transl Oncol. 2011 Feb;13(2):121-32. doi: 10.1007/s12094-011-0629-6. Clin Transl Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21324801 Review.
-
Long-term results of weekly paclitaxel carboplatin induction therapy: an effective and well-tolerated treatment in patients with platinum-resistant ovarian cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2013 Apr;49(6):1254-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.11.027. Epub 2012 Dec 29. Eur J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23276720 Clinical Trial.
-
Medical therapy of advanced malignant epithelial tumours of the ovary.Forum (Genova). 2000 Oct-Dec;10(4):323-32. Forum (Genova). 2000. PMID: 11535983 Review.
Cited by
-
What Is New in the Diagnosis and Management of Penile Cancer?Indian J Surg Oncol. 2017 Sep;8(3):379-384. doi: 10.1007/s13193-016-0613-2. Epub 2017 Feb 27. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 36118381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development and Verification of Prognostic Nomogram for Penile Cancer Based on the SEER Database.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Apr 4;2022:8752388. doi: 10.1155/2022/8752388. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35419456 Free PMC article.
-
Adjuvant pelvic radiation is associated with improved survival and decreased disease recurrence in pelvic node-positive penile cancer after lymph node dissection: A multi-institutional study.Urol Oncol. 2017 Oct;35(10):605.e17-605.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Urol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28666722 Free PMC article.
-
Inguinal lymph node dissection for penile cancer: a contemporary review.Transl Androl Urol. 2020 Dec;9(6):3210-3218. doi: 10.21037/tau.2019.08.37. Transl Androl Urol. 2020. PMID: 33457292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extent of pelvic lymph node dissection in penile cancer may impact survival.World J Urol. 2016 Mar;34(3):353-9. doi: 10.1007/s00345-015-1593-5. Epub 2015 May 31. World J Urol. 2016. PMID: 26026817
References
-
- Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Maldonado JL, Pow-sang J, Giuliano AR. Incidence trends in primary malignant penile cancer. Urol Oncol. 2007;25:361–7. - PubMed
-
- Misra S, Chaturvedi A, Misra NC. Penile carcinoma: A challenge for the developing world. Lancet Oncol. 2004;5:240–7. - PubMed
-
- Ficarra V, Akduman B, Bouchot O, Palou J, Tobias-Machado M. Prognostic Factors in Penile Cancer. Urology. 2010;76:S66–73. - PubMed
-
- Novara G, Galfano A, De Marco V, Artibani W, Ficarra V. Prognostic factors in squamous cell carcinoma of the penis. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2007;4:140–6. - PubMed
-
- Ravi R. Morbidity following groin dissection for penile carcinoma. Br J Urol. 1993;72:941–5. - PubMed