Mechanisms underlying the tissue-specific and regulated activity of the Gnrhr promoter in mammals
- PMID: 23248618
- PMCID: PMC3521148
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2012.00162
Mechanisms underlying the tissue-specific and regulated activity of the Gnrhr promoter in mammals
Abstract
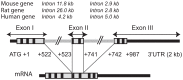
The GnRH receptor (GnRHR) plays a central role in the development and maintenance of reproductive function in mammals. Following stimulation by GnRH originating from the hypothalamus, GnRHR triggers multiple signaling events that ultimately stimulate the synthesis and the periodic release of the gonadotropins, luteinizing-stimulating hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormones (FSH) which, in turn, regulate gonadal functions including steroidogenesis and gametogenesis. The concentration of GnRHR at the cell surface is essential for the amplitude and the specificity of gonadotrope responsiveness. The number of GnRHR is submitted to strong regulatory control during pituitary development, estrous cycle, pregnancy, lactation, or after gonadectomy. These modulations take place, at least in part, at the transcriptional level. To analyze this facet of the reproductive function, the 5' regulatory sequences of the gene encoding the GnRHR have been isolated and characterized through in vitro and in vivo approaches. This review summarizes results obtained with the mouse, rat, human, and ovine promoters either by transient transfection assays or by means of transgenic mice.
Keywords: GnRH receptor; gonadotrope cell lines; homeodomain proteins; promoter regions; steroidogenic factor 1; transcription; transgenic mice.
Figures

References
-
- Achermann J. C., Ito M., Ito M., Hindmarsh P. C., Jameson J. L. (1999). A mutation in the gene encoding steroidogenic factor-1 causes XY sex reversal and adrenal failure in humans. Nat. Genet. 22 125–126 - PubMed
-
- Achermann J. C., Weiss J., Lee E. J., Jameson J. L. (2001). Inherited disorders of the gonadotropin hormones. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 179 89–96 - PubMed
-
- Alarid E. T., Windle J. J., Whyte D. B., Mellon P. L. (1996). Immortalization of pituitary cells at discrete stages of development by directed oncogenesis in transgenic mice. Development 122 3319–3329 - PubMed
-
- Albarracin C. T., Frosch M. P., Chin W. W. (1999). The gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor gene promoter directs pituitary-specific oncogene expression in transgenic mice. Endocrinology 140 2415–2421 - PubMed
-
- Albarracin C. T., Kaiser U. B., Chin W. W. (1994). Isolation and characterization of the 5′-flanking region of the mouse gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor gene. Endocrinology 135 2300–2306 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

