Mechanisms of arterial remodeling: lessons from genetic diseases
- PMID: 23248645
- PMCID: PMC3521155
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00290
Mechanisms of arterial remodeling: lessons from genetic diseases
Abstract
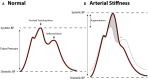
Vascular disease is still the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the Western world, and the primary cause of myocardial infarction, stroke, and ischemia. The biology of vascular disease is complex and still poorly understood in terms of causes and consequences. Vascular function is determined by structural and functional properties of the arterial vascular wall. Arterial stiffness, that is a pathological alteration of the vascular wall, ultimately results in target-organ damage and increased mortality. Arterial remodeling is accelerated under conditions that adversely affect the balance between arterial function and structure such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, inflammatory disease, lifestyle aspects (smoking), drugs (vitamin K antagonists), and genetic abnormalities [e.g., pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE), Marfan's disease]. The aim of this review is to provide an overview of the complex mechanisms and different factors that underlie arterial remodeling, learning from single gene defect diseases like PXE, and PXE-like, Marfan's disease and Keutel syndrome in vascular remodeling.
Keywords: arterial remodeling; calcification; genetic disease; vitamin K; vitamin K-antagonists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Mechanisms of Vascular Remodeling Following Arterial Injury].Kardiologiia. 2015;55(7):63-77. doi: 10.18565/cardio.2015.7.63-77. Kardiologiia. 2015. PMID: 26688928 Review. Russian.
-
Relationship between ankle brachial index and arterial remodeling in pseudoxanthoma elasticum.J Vasc Surg. 2011 Nov;54(5):1390-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.04.041. Epub 2011 Jul 1. J Vasc Surg. 2011. PMID: 21723076 Free PMC article.
-
Arterial stiffening and thickening in patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum.Atherosclerosis. 2018 Mar;270:160-165. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.02.006. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Atherosclerosis. 2018. PMID: 29432933
-
Arterial Stiffness: A Nexus between Cardiac and Renal Disease.Cardiorenal Med. 2014 Apr;4(1):60-71. doi: 10.1159/000360867. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Cardiorenal Med. 2014. PMID: 24847335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early arterial calcification does not correlate with bone loss in pseudoxanthoma elasticum.Bone. 2017 Oct;103:88-92. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2017.06.017. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Bone. 2017. PMID: 28658601
Cited by
-
Medial vascular calcification revisited: review and perspectives.Eur Heart J. 2014 Jun 14;35(23):1515-25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu163. Epub 2014 Apr 16. Eur Heart J. 2014. PMID: 24740885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design considerations for engineering 3D models to study vascular pathologies in vitro.Acta Biomater. 2021 Sep 15;132:114-128. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.02.031. Epub 2021 Feb 27. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33652164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
24-hour central blood pressure and immune system activation in adolescents with primary hypertension - a preliminary study.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2022;47(2):160-167. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2022.117929. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36751390 Free PMC article.
-
The Angiotensin AT2 Receptor: From a Binding Site to a Novel Therapeutic Target.Pharmacol Rev. 2022 Oct;74(4):1051-1135. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.120.000281. Pharmacol Rev. 2022. PMID: 36180112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PVAT adipocyte: energizing, modulating, and structuring vascular function during normotensive and hypertensive states.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025 Jun 1;328(6):H1204-H1217. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00093.2025. Epub 2025 Apr 18. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40250838 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

