Somatic mutagenesis in autoimmunity
- PMID: 23249093
- PMCID: PMC3743419
- DOI: 10.3109/08916934.2012.757597
Somatic mutagenesis in autoimmunity
Abstract
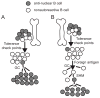
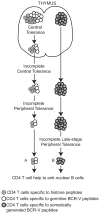
Our laboratory investigates systemic autoimmune disease in the context of mouse models of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). SLE is associated with high titers of serum autoantibodies of the IgG class that are predominantly directed against nuclear antigens, with pathological manifestations that are considered by many to be characteristic of an immune-complex mediated disease. In this review, we focus on the known and potential roles of somatic mutagenesis in SLE. We will argue that anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) arise predominantly from nonautoreactive B cells that are transformed into autoreactive cells by the process of somatic hypermutation (SHM), which is normally associated with affinity maturation during the germinal center reaction. We will also discuss the role of SHM in creating antigenic peptides in the V region of the B cell receptor (BCR) and its potential to open an avenue of unregulated T cell help to autoreactive B cells. Finally, we will end this review with new experimental evidence suggesting that spontaneous somatic mutagenesis of genes that regulate B cell survival and activation is a rate-limiting causative factor in the development of ANA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
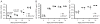
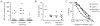

References
-
- Kotzin BL. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Cell. 1996;85:303–306. - PubMed
-
- Theofilopoulos AN, Dixon FJ. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Advances in immunology. 1985;37:269–390. - PubMed
-
- Goodnow CC. Multistep pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Cell. 2007;130:25–35. - PubMed
-
- Wardemann H, Yurasov S, Schaefer A, Young JW, Meffre E, Nussenzweig MC. Predominant autoantibody production by early human B cell precursors. Science. 2003;301:1374–1377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
