Electrochemistry at the edge of a single graphene layer in a nanopore
- PMID: 23249127
- PMCID: PMC3551991
- DOI: 10.1021/nn305400n
Electrochemistry at the edge of a single graphene layer in a nanopore
Abstract
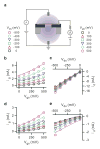
We study the electrochemistry of single layer graphene edges using a nanopore-based structure consisting of stacked graphene and Al(2)O(3) dielectric layers. Nanopores, with diameters ranging from 5 to 20 nm, are formed by an electron beam sculpting process on the stacked layers. This leads to a unique edge structure which, along with the atomically thin nature of the embedded graphene electrode, demonstrates electrochemical current densities as high as 1.2 × 10(4) A/cm(2). The graphene edge embedded structure offers a unique capability to study the electrochemical exchange at an individual graphene edge, isolated from the basal plane electrochemical activity. We also report ionic current modulation in the nanopore by biasing the embedded graphene terminal with respect to the electrodes in the fluid. The high electrochemical specific current density for a graphene nanopore-based device can have many applications in sensitive chemical and biological sensing, and energy storage devices.
Figures

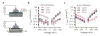
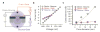

References
-
- Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV, Grigorieva IV, Firsov AA. Electric Field Effect in Atomically Thin Carbon Films. Science. 2004;10 :306, 666–669. - PubMed
-
- Bolotin KI, Sikes KJ, Jiang Z, Klima M, Fudenberg G, Hone J, Kim P, Stormer HL. Ultrahigh Electron Mobility in Suspended Graphene. Solid State Commun. 2008;146:351–355.
-
- Balandin AA. Thermal Properties of Graphene and Nanostructured Carbon Materials. Nat Mater. 2011;10:569–581. - PubMed
-
- Mak KF, Shan J, Heinz TF. Electronic Structure of Few-Layer Graphene: Experimental Demonstration of Strong Dependence on Stacking Sequence. Phys Rev Lett. 2010;104:176404. - PubMed
-
- Pumera M. Electrochemistry of Graphene: New Horizons for Sensing and Energy Storage. Chem Rec. 2009;9:211–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

