Synergetic downregulation of 67 kDa laminin receptor by the green tea (Camellia sinensis) secondary plant compound epigallocatechin gallate: a new gateway in metastasis prevention?
- PMID: 23249430
- PMCID: PMC3536572
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-12-258
Synergetic downregulation of 67 kDa laminin receptor by the green tea (Camellia sinensis) secondary plant compound epigallocatechin gallate: a new gateway in metastasis prevention?
Abstract
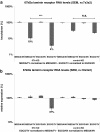
Background: In traditional Chinese medicine, green tea is considered to have a life-prolonging effect, possibly as a result of its rich content of antioxidant tea polyphenols, and hence has the potential to prevent cancer. This study investigated the role of the major tea secondary plant compound epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) for its inhibitory effects on the metastasis-associated 67 kDa laminin receptor (67LR).
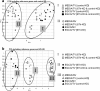
Methods: To clarify the impact of EGCG on siRNA-silenced expression of 67LR, we applied an adenoviral-based intestinal in vitro knockdown model, porcine IPEC-J2 cells. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was performed to analyze 67LR gene expression following treatment with physiological and pharmacological concentrations of EGCG (1.0 g/l, 0.1 g/l, 0.02 g/l and 0.002 g/l).
Results: We report co-regulation of EGCG and 67LR, which is known to be an EGCG receptor. siRNA selectively and highly significantly suppressed expression of 67LR under the impact of EGCG in a synergetic manner.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that 67LR expression is regulated by EGCG via a negative feedback loop. The explicit occurrence of this effect in synergy with a small RNA pathway and a plant-derived drug reveals a new mode of action. Our findings may help to provide insights into the many unsolved health-promoting activities of other natural pharmaceuticals.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epigallocatechin Gallate Induces Upregulation of LDL Receptor via the 67 kDa Laminin Receptor-Independent Pathway in HepG2 Cells.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020 Apr;64(7):e1901036. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201901036. Epub 2020 Feb 5. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020. PMID: 31978263
-
Attenuated migration by green tea extract (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG): involvement of 67 kDa laminin receptor internalization in macrophagic cells.Food Funct. 2014 Aug;5(8):1915-9. doi: 10.1039/c4fo00143e. Food Funct. 2014. PMID: 24953562
-
Green tea (-)-epigallocatechin gallate inhibits insulin stimulation of 3T3-L1 preadipocyte mitogenesis via the 67-kDa laminin receptor pathway.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009 Jul;297(1):C121-32. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00272.2008. Epub 2009 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19176763
-
Molecular Targets of Epigallocatechin-Gallate (EGCG): A Special Focus on Signal Transduction and Cancer.Nutrients. 2018 Dec 6;10(12):1936. doi: 10.3390/nu10121936. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30563268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
67-kDa Laminin Receptor-Mediated Cellular Sensing System of Green Tea Polyphenol EGCG and Functional Food Pairing.Molecules. 2022 Aug 11;27(16):5130. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165130. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014370 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of nutrition in PCB-induced vascular inflammation.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2014 May;21(10):6410-8. doi: 10.1007/s11356-013-1549-5. Epub 2013 Feb 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2014. PMID: 23417440 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

