Dual functions of Insig proteins in cholesterol homeostasis
- PMID: 23249523
- PMCID: PMC3564778
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-11-173
Dual functions of Insig proteins in cholesterol homeostasis
Abstract
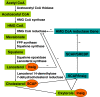
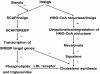
The molecular mechanism of how cells maintain cholesterol homeostasis has become clearer for the understanding of complicated association between sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs), SREBP cleavage-activating protein (SCAP), 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA reductase) and Insuin induced-genes (Insigs). The pioneering researches suggested that SREBP activated the transcription of genes encoding HMG-CoA reductase and all of the other enzymes involved in the synthesis of cholesterol and lipids. However, SREBPs can not exert their activities alone, they must form a complex with another protein, SCAP in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and translocate to Golgi. Insigs are sensors and mediators that regulate cholesterol homeostasis through binding to SCAP and HMG-CoA reductase in diverse tissues such as adipose tissue and liver, as well as the cultured cells. In this article, we aim to review on the dual functions of Insig protein family in cholesterol homeostasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insulin-induced gene: a new regulator in lipid metabolism.Peptides. 2010 Nov;31(11):2145-50. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.07.020. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Peptides. 2010. PMID: 20817058 Review.
-
Isolation of sterol-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells with genetic deficiencies in both Insig-1 and Insig-2.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 1;280(26):25242-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M502989200. Epub 2005 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15866869
-
PAQR3 modulates cholesterol homeostasis by anchoring Scap/SREBP complex to the Golgi apparatus.Nat Commun. 2015 Aug 27;6:8100. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9100. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26311497 Free PMC article.
-
Direct binding to sterols accelerates endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of HMG CoA reductase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Feb 13;121(7):e2318822121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2318822121. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38319967 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective on Cholesterol Homeostasis: The Central Role of Scap.Annu Rev Biochem. 2018 Jun 20;87:783-807. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-011852. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Annu Rev Biochem. 2018. PMID: 28841344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation, sequence characterization, and tissue transcription profiles of two novel buffalo genes: INSIG1 and INSIG2.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2014 Jan;46(1):33-41. doi: 10.1007/s11250-013-0443-y. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2014. PMID: 23860946
-
The cellular function of SCAP in metabolic signaling.Exp Mol Med. 2020 May;52(5):724-729. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-0430-0. Epub 2020 May 8. Exp Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32385422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic Changes in Liver of Young Bulls Caused by Diets Low in Mineral and Protein Contents and Supplemented with n-3 Fatty Acids and Conjugated Linoleic Acid.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 8;11(12):e0167747. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167747. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27930681 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Metabolism in Bone Development and Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 26;21(23):8992. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238992. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33256181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The unfolded protein response and hepatic lipid metabolism in non alcoholic fatty liver disease.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Nov;203:107401. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107401. Epub 2019 Aug 13. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31419516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yokoyama C, Wang X, Briggs MR, Admon A, Wu J, Hua X, Goldstein JL, Brown MS. SREBP-1, a basic helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper protein that controls transcription of the LDL receptor gene. Cell. 1993;75:187–197. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Liu F, Millette CF, Kilpatrick DL. Expression of a novel, sterol-insensitive form of sterol regulatory element binding protein 2 (SREBP2) in male germ cells suggests important cell- and stage-specific functions for SREBP targets during spermatogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;24:8478–8490. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

