The R0 package: a toolbox to estimate reproduction numbers for epidemic outbreaks
- PMID: 23249562
- PMCID: PMC3582628
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6947-12-147
The R0 package: a toolbox to estimate reproduction numbers for epidemic outbreaks
Abstract
Background: Several generic methods have been proposed to estimate transmission parameters during an outbreak, especially the reproduction number. However, as of today, no dedicated software exists that implements these methods and allow comparisons.
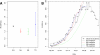
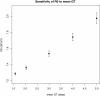
Results: A review of generic methods used to estimate transmissibility parameters during outbreaks was carried out. Most methods used the epidemic curve and the generation time distribution. Two categories of methods were available: those estimating the initial reproduction number, and those estimating a time dependent reproduction number. We implemented five methods as an R library, developed sensitivity analysis tools for each method and provided numerical illustrations of their use. A comparison of the performance of the different methods on simulated datasets is reported.
Conclusions: This software package allows a standardized and extensible approach to the estimation of the reproduction number and generation interval distribution from epidemic curves.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Improved inference of time-varying reproduction numbers during infectious disease outbreaks.Epidemics. 2019 Dec;29:100356. doi: 10.1016/j.epidem.2019.100356. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Epidemics. 2019. PMID: 31624039 Free PMC article.
-
High reproduction number of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in nosocomial outbreaks: mathematical modelling in Saudi Arabia and South Korea.J Hosp Infect. 2018 Jun;99(2):162-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2017.09.017. Epub 2017 Sep 25. J Hosp Infect. 2018. PMID: 28958834 Free PMC article.
-
Complexity of the Basic Reproduction Number (R0).Emerg Infect Dis. 2019 Jan;25(1):1-4. doi: 10.3201/eid2501.171901. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30560777 Free PMC article.
-
The estimation of the basic reproduction number for infectious diseases.Stat Methods Med Res. 1993;2(1):23-41. doi: 10.1177/096228029300200103. Stat Methods Med Res. 1993. PMID: 8261248 Review.
-
Statistical Estimation of the Reproductive Number From Case Notification Data.Am J Epidemiol. 2021 Apr 6;190(4):611-620. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwaa211. Am J Epidemiol. 2021. PMID: 33034345 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiological profile and transmission dynamics of COVID-19 in the Philippines.Epidemiol Infect. 2020 Sep 15;148:e204. doi: 10.1017/S0950268820002137. Epidemiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 32928322 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial and temporal regularization to estimate COVID-19 reproduction number R(t): Promoting piecewise smoothness via convex optimization.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 20;15(8):e0237901. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237901. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32817697 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of the basic reproduction number (R0) for the novel coronavirus disease in Sri Lanka.Virol J. 2020 Oct 7;17(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12985-020-01411-0. Virol J. 2020. PMID: 33028382 Free PMC article.
-
Does the data tell the true story? A modelling assessment of early COVID-19 pandemic suppression and mitigation strategies in Ghana.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 29;16(10):e0258164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258164. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34714857 Free PMC article.
-
Ziegler and Nichols meet Kermack and McKendrick: Parsimony in dynamic models for epidemiology.Comput Chem Eng. 2022 Jan;157:107615. doi: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2021.107615. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Comput Chem Eng. 2022. PMID: 34961800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Surveillance during an Influenza Pandemic. 2009. http://www.who.int/csr/disease/swineflu/global_pandemic_influenza_survei....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

