[Construction of a CD147 lentiviral expression vector and establishment of its stably transfected A549 cell line]
- PMID: 23249715
- PMCID: PMC6000049
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2012.12.03
[Construction of a CD147 lentiviral expression vector and establishment of its stably transfected A549 cell line]
Abstract
Background and objective: CD147, a type of transmembrane glycoprotein embedded on the surface of tumor cells, can promote tumor invasion and metastasis. This aim of this study is to construct a CD147 lentiviral expression vector, establish its stably transfected A549 cell line, and observe the effect of CD147 on MMP-9 proliferation as well as on the invasive ability of human lung adenocarcinoma cells.
Methods: Full-length CD147 gene was amplified by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), inserted into a pEGFP vector to construct pEGFP-CD147 and pEGFP vectors, and then transfected into 293FT cells to precede the lentivirus equipment package. Subsequently, we collected the lentivirus venom to infect the A549 cells and establish a stable, overexpressed cell line named A549-CD147. The mRNA expression of MMP-9 was examined by RT-PCR. The proliferation and invasive ability of the human lung cancer cells before and after transfection were examined by the CCK-8 and Transwell methods.
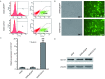
Results: A CD147 lentiviral expression vector (pEGFP-CD147) was successfully constructed by restrictive enzyme digestion and plasmid sequencing. RT-PCR and Western blot analyses revealed increased mRNA and protein expression of CD147 gene in cells transfected with pEGFP-CD147 compared with the control groups. Therefore, the A549-CD147 cell line was successfully established through the experiment. The mRNA expression of MMP-9 also significantly increased after the upregulation of CD147 expression. Meanwhile, CCK-8 and Transwell assays indicated that the proliferation and invasive ability significantly increased in the A549-CD147 cells.
Conclusions: A lentiviral CD147 expression vector and its A549 cell line (A549-CD14) were successfully constructed. CD147 overexpression upregulated the protein expression of MMP-9, and strengthened the proliferation and invasive ability of human lung adenocarcinoma cells.
背景与目的: CD147是一类位于肿瘤细胞膜表面的跨膜糖蛋白,可促进肿瘤的浸润和转移。本研究拟构建CD147慢病毒表达载体,建立稳定过表达CD147的人肺腺癌A549细胞系,观察过表达CD147后对MMP-9及细胞增殖、侵袭能力的影响。
方法: RT-PCR扩增CD147基因全长序列,将序列插入pEGFP载体,构建pEGFP-CD147慢病毒表达载体,随后转入293FT细胞中进行慢病毒包装,用获得的慢病毒毒液感染人肺腺癌细胞系A549,建立稳定过表达CD147的A549细胞系。Real-time PCR检测MMP-9的变化情况,CCK-8及Transwell法检测人肺腺癌细胞增殖、侵袭能力的变化。
结果: 经限制性内切酶鉴定及测序分析,成功构建了pEGFP-CD147慢病毒表达载体质粒。Real-time PCR和Western blot检测显示,与对照组相比,转染pEGFP-CD147慢病毒表达载体组的细胞,CD147的表达在mRNA和蛋白两个水平均增高,成功建立了A549-CD147细胞系。上调CD147的表达后,MMP-9的mRNA表达水平明显升高。同时,A549-CD147细胞增殖和侵袭能力明显增加(P < 0.05)。
结论: 成功构建CD147慢病毒表达载体和A549-CD147细胞系,过表达CD147可上调MMP-9的表达,增强人肺腺癌细胞的增殖和侵袭能力。
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Establishment of a lung cancer A549 cell line stable over-expressing integrin linked kinase protein and its biological activity].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Apr;28(4):340-3. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22482400 Chinese.
-
RNAi-mediated silencing of CD147 inhibits tumor cell proliferation, invasion and increases chemosensitivity to cisplatin in SGC7901 cells in vitro.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jun 3;29(1):61. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-61. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20525232 Free PMC article.
-
[Impact of siRNA-mediated down-regulation of CD147 on human breast cancer cells].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Oct;44(10):734-8. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26702532 Chinese.
-
[Construction of A eukaryotic expression vector carrying the iNOS gene and its effect on A549 lung cancer cells].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2012 May;15(5):260-6. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2012.05.02. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22613330 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Importance of N-glycosylation on CD147 for its biological functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Apr 15;15(4):6356-77. doi: 10.3390/ijms15046356. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24739808 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The biological function and clinical utilization of CD147 in human diseases: a review of the current scientific literature.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Sep 29;15(10):17411-41. doi: 10.3390/ijms151017411. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25268615 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Biswas C, Zhang Y, Decastro R, et al. The human tumor cell-derived collagenase stimulatory factor (Renamed EMMPRIN) is a member of the immunoglobulin supperfamily. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/%207812975. Cancer Res. 1995;55(2):434–439. [Biswas C, Zhang Y, Decastro R, et al. The human tumor cell-derived collagenase stimulatory factor (Renamed EMMPRIN) is a member of the immunoglobulin supperfamily. Cancer Res, 1995, 55(2): 434-439.] - PubMed
-
- Kanekura T, Chen X, Kanzaki T. Basigi (CDl47) is expressed on melanoma cells and induces tumor cell invasion by stimulating production of matrix metalloproteinases by fibroblasts. Int J Cancer. 2002;99(4):520–528. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-0215. [Kanekura T, Chen X, Kanzaki T. Basigi (CDl47) is expressed on melanoma cells and induces tumor cell invasion by stimulating production of matrix metalloproteinases by fibroblasts. Int J Cancer, 2002, 99(4): 520-528.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kanekura T, Chen X. CD147 promotes progression of malignant melanoma and other cancers. J Dermatol Sci. 2010;57(3):149–154. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2009.12.008. [Kanekura T, Chen X. CD147 promotes progression of malignant melanoma and other cancers. J Dermatol Sci, 2010, 57(3): 149-154.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zheng HC, Takahashi H, Murai Y. Up-regulated EMMPRIN/CD147 might contribute to growth and angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma: a good marker for local invasion and prognosis. Br J Cancer. 2006;95(10):1371–1378. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603425. [Zheng HC, Takahashi H, Murai Y. Up-regulated EMMPRIN/CD147 might contribute to growth and angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma: a good marker for local invasion and prognosis. Br J Cancer, 2006, 95(10): 1371-1378.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

