Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats
- PMID: 23249747
- PMCID: PMC3543092
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.035667.112
Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats
Erratum in
- RNA. 2013 Mar;19(3):426
Abstract
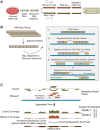
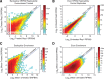
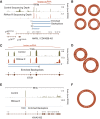
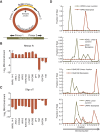
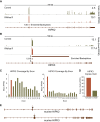
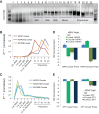
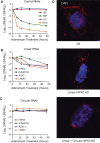
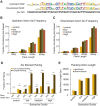
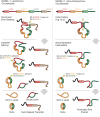
Circular RNAs composed of exonic sequence have been described in a small number of genes. Thought to result from splicing errors, circular RNA species possess no known function. To delineate the universe of endogenous circular RNAs, we performed high-throughput sequencing (RNA-seq) of libraries prepared from ribosome-depleted RNA with or without digestion with the RNA exonuclease, RNase R. We identified >25,000 distinct RNA species in human fibroblasts that contained non-colinear exons (a "backsplice") and were reproducibly enriched by exonuclease degradation of linear RNA. These RNAs were validated as circular RNA (ecircRNA), rather than linear RNA, and were more stable than associated linear mRNAs in vivo. In some cases, the abundance of circular molecules exceeded that of associated linear mRNA by >10-fold. By conservative estimate, we identified ecircRNAs from 14.4% of actively transcribed genes in human fibroblasts. Application of this method to murine testis RNA identified 69 ecircRNAs in precisely orthologous locations to human circular RNAs. Of note, paralogous kinases HIPK2 and HIPK3 produce abundant ecircRNA from their second exon in both humans and mice. Though HIPK3 circular RNAs contain an AUG translation start, it and other ecircRNAs were not bound to ribosomes. Circular RNAs could be degraded by siRNAs and, therefore, may act as competing endogenous RNAs. Bioinformatic analysis revealed shared features of circularized exons, including long bordering introns that contained complementary ALU repeats. These data show that ecircRNAs are abundant, stable, conserved and nonrandom products of RNA splicing that could be involved in control of gene expression.
Figures
References
-
- Capel B, Swain A, Nicolis S, Hacker A, Walter M, Koopman P, Goodfellow P, Lovell-Badge R 1993. Circular transcripts of the testis-determining gene Sry in adult mouse testis. Cell 73: 1019–1030 - PubMed
-
- Chen CY, Sarnow P 1995. Initiation of protein synthesis by the eukaryotic translational apparatus on circular RNAs. Science 268: 415–417 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
