Biceps skin-fold thickness may detect and predict early lipoatrophy in HIV-infected children
- PMID: 23249919
- PMCID: PMC4000309
- DOI: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3182814b30
Biceps skin-fold thickness may detect and predict early lipoatrophy in HIV-infected children
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of potentially stigmatizing lipoatrophy in children receiving antiretroviral therapy in Southern Africa is high, affecting around a third of children. Early diagnosis of lipoatrophy is essential for effective intervention to arrest progression.
Methods: Prepubertal children receiving antiretroviral therapy were recruited from a hospital-based family HIV clinic in Cape Town and followed up prospectively. Lipoatrophy was identified and graded by consensus between 2 HIV pediatricians. A dietician performed anthropometric measurements of trunk and limb fat. Anthropometric measurements in children with and without lipoatrophy were compared using multivariable linear regression adjusting for age and gender. The most discerning anthropometric indicators of lipoatrophy underwent receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. The precision of anthropometric measurements performed by an inexperienced healthcare worker was compared with that of a research dietician.
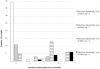
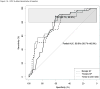
Results: Of 100 recruits, 36 had lipoatrophy at baseline and a further 9 developed lipoatrophy by 15-month follow-up. Annual incidence of lipoatrophy was 12% (confidence interval [CI]: 5-20%) per person-year of follow-up. A biceps skin-fold thickness <5 mm at baseline had a sensitivity of 89% (CI: 67-100%) and a specificity of 60% (CI: 46-75%) for predicting development of lipoatrophy by 15-month follow-up. Negative and positive predictive values were 97% (CI: 91-100%) and 32% (CI: 14-50%).
Conclusion: Biceps skin-fold thickness <5 mm in prepubertal children exposed to thymidine analogue-based antiretroviral therapy may be a useful screening tool to identify children who are likely to develop lipoatrophy. The variation in precision of measurements performed by an inexperienced healthcare worker only marginally impacted performance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
The content of this publication does not necessarily reflect the views or policies of NIAID, nor does mention of trade names, commercial projects, or organizations imply endorsement by the US Government.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High prevalence of lipoatrophy in pre-pubertal South African children on antiretroviral therapy: a cross-sectional study.BMC Pediatr. 2012 Nov 23;12:183. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-12-183. BMC Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 23176441 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of lipoatrophy in human immunodeficiency virus-1-infected children treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006 May;25(5):427-31. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000215003.32256.aa. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2006. PMID: 16645507
-
Correlates of risk of adipose tissue alterations and their modifications over time in HIV-1-infected women treated with antiretroviral therapy.Antivir Ther. 2003 Aug;8(4):347-54. Antivir Ther. 2003. PMID: 14518704
-
Antiretroviral-therapy-associated lipoatrophy: current status and future directions.Sex Health. 2005;2(3):153-63. doi: 10.1071/sh04058. Sex Health. 2005. PMID: 16335543 Review.
-
Disorders of body fat distribution in HIV-1-infected patients.AIDS Rev. 2009 Jul-Sep;11(3):126-34. AIDS Rev. 2009. PMID: 19654854 Review.
Cited by
-
A Randomized Comparison of Anthropomorphic Changes With Preferred and Alternative Efavirenz-Based Antiretroviral Regimens in Diverse Multinational Settings.Open Forum Infect Dis. 2015 Jun 24;2(3):ofv095. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofv095. eCollection 2015 Sep. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26213694 Free PMC article.
-
Lipoatrophy/lipohypertrophy outcomes after antiretroviral therapy switch in children in the UK/Ireland.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 4;13(4):e0194132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194132. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29617438 Free PMC article.
-
Health-Related Physical Fitness Evaluation in HIV-Diagnosed Children and Adolescents: A Scoping Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024 Apr 25;21(5):541. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21050541. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38791753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. [Accessed 15 September 2011];Forecasting antiretroviral demand. 2010 http://www.who.int/hiv/amds/forecasting/en/index4.html.
-
- South African National Department of Health. The South African Antiretroviral Treatment Guidelines. Pretoria: SANDoH; 2010.
-
- Shlay JC, Sharma S, Peng G, Gibert CL, Grunfeld C. Long-term subcutaneous tissue changes among antiretroviral-naive persons initiating stavudine, zidovudine, or abacavir with lamivudine. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2008 May 1;48(1):53–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1U19AI53217-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI36214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027670/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI053217/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R43 AI093318/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069521/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI062758/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AI36214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R43 AI093318-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01AI069521-01/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI 27670/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1 UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214-16/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24-TW007988-01/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01AI069521-02/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI064086/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI62758/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01AI069521-03/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 TW007988/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 5U01AI069521-04/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024975/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WTX055734/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- AI69432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

