Immunogenicity in mice and non-human primates of the Group A Streptococcal J8 peptide vaccine candidate conjugated to CRM197
- PMID: 23249976
- PMCID: PMC3891704
- DOI: 10.4161/hv.23224
Immunogenicity in mice and non-human primates of the Group A Streptococcal J8 peptide vaccine candidate conjugated to CRM197
Abstract
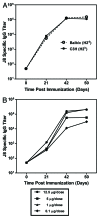
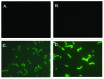
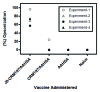
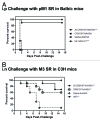
Vaccine development for Group A streptococcal (GAS) infection has been extensively focused on the N-terminal hypervariable or the C-terminal conserved regions of the M protein, a major virulence factor of GAS. We evaluated the immunogenicity and functional activity of the conserved C-terminal peptide vaccine candidate, J8, conjugated to CRM197, in two mouse strains: C3H (H2(k)) and Balb/c (H2(d)), and in rhesus macaques. Mice were immunized with J8-CRM197 formulated with Amorphous Aluminum Hydroxyphosphate Sulfate Adjuvant (AAHSA), and non-human primates were immunized with J8-CRM197 formulated with AAHSA, ISCOMATRIX (TM) adjuvant, or AAHSA/ISCOMATRIX adjuvant. J8-CRM197 was immunogenic in mice from both H2(k) and H2(d) backgrounds, and the antibodies generated bound to the surface of four different GAS serotypes and had functional bacterial opsonic activity. Mice immunized with J8-CRM197/AAHSA demonstrated varying degrees of protection from lethal challenge. We also demonstrated that J8-CRM197 is immunogenic in non-human primates. Our data confirm the utility of J8 as a potential GAS vaccine candidate and demonstrate that CRM197 is an acceptable protein carrier for this peptide.
Keywords: Group A streptococcus; Streptococcus pyogenes; immunogenicity; mice; non-human primates; vaccine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Physicochemical characterisation, immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a lead streptococcal vaccine: progress towards Phase I trial.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 23;7(1):13786. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14157-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29062085 Free PMC article.
-
Differing Efficacies of Lead Group A Streptococcal Vaccine Candidates and Full-Length M Protein in Cutaneous and Invasive Disease Models.mBio. 2016 Jun 14;7(3):e00618-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00618-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27302756 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced protection against Streptococcus pyogenes infection by intranasal vaccination with a dual antigen component M protein/SfbI lipid core peptide vaccine formulation.Vaccine. 2007 Feb 26;25(10):1789-97. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.11.031. Epub 2006 Nov 30. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17229503
-
Lipid core peptide technology and group A streptococcal vaccine delivery.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2004 Feb;3(1):43-58. doi: 10.1586/14760584.3.1.43. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2004. PMID: 14761243 Review.
-
Strategic development of the conserved region of the M protein and other candidates as vaccines to prevent infection with group A streptococci.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015;14(11):1459-70. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2015.1081817. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015. PMID: 26485214 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of built-in adjuvants for epitope-based vaccines.PeerJ. 2019 Jan 14;6:e6185. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6185. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 30656066 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus: An organism causing diseases beyond neglect.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 May 21;14(5):e0008095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008095. eCollection 2020 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32437344 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Preclinical evaluations of peptide-conjugate vaccines targeting the antigenic domain-2 of glycoprotein B of human cytomegalovirus.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016 Aug 2;12(8):2106-2112. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2016.1164376. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2016. PMID: 26986197 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of the classical Lancefield assay of group A streptococcal killing to reduce inter-donor variation.J Microbiol Methods. 2016 May;124:69-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2016.03.015. Epub 2016 Mar 24. J Microbiol Methods. 2016. PMID: 27030640 Free PMC article.
-
Antibodies to the conserved region of the M protein and a streptococcal superantigen cooperatively resolve toxic shock-like syndrome in HLA-humanized mice.Sci Adv. 2019 Sep 4;5(9):eaax3013. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax3013. eCollection 2019 Sep. Sci Adv. 2019. PMID: 31517054 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
