Roles of Bmp4 during tooth morphogenesis and sequential tooth formation
- PMID: 23250216
- PMCID: PMC3597212
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.081927
Roles of Bmp4 during tooth morphogenesis and sequential tooth formation
Abstract
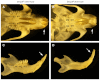
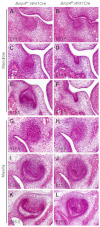
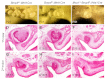
Previous studies have suggested that Bmp4 is a key Msx1-dependent mesenchymal odontogenic signal for driving tooth morphogenesis through the bud-to-cap transition. Whereas all tooth germs were arrested at the bud stage in Msx1(-/-) mice, we show that depleting functional Bmp4 mRNAs in the tooth mesenchyme, through neural crest-specific gene inactivation in Bmp4(f/f);Wnt1Cre mice, caused mandibular molar developmental arrest at the bud stage but allowed maxillary molars and incisors to develop to mineralized teeth. We found that expression of Osr2, which encodes a zinc finger protein that antagonizes Msx1-mediated activation of odontogenic mesenchyme, was significantly upregulated in the molar tooth mesenchyme in Bmp4(f/f);Wnt1Cre embryos. Msx1 heterozygosity enhanced maxillary molar developmental defects whereas Osr2 heterozygosity partially rescued mandibular first molar morphogenesis in Bmp4(f/f);Wnt1Cre mice. Moreover, in contrast to complete lack of supernumerary tooth initiation in Msx1(-/-)Osr2(-/-) mice, Osr2(-/-)Bmp4(f/f);Wnt1Cre compound mutant mice exhibited formation and subsequent arrest of supernumerary tooth germs that correlated with downregulation of Msx1 expression in the tooth mesenchyme. In addition, we found that the Wnt inhibitors Dkk2 and Wif1 were much more abundantly expressed in the mandibular than maxillary molar mesenchyme in wild-type embryos and that Dkk2 expression was significantly upregulated in the molar mesenchyme in Bmp4(f/f);Wnt1Cre embryos, which correlated with the dramatic differences in maxillary and mandibular molar phenotypes in Bmp4(f/f);Wnt1Cre mice. Together, these data indicate that Bmp4 signaling suppresses tooth developmental inhibitors in the tooth mesenchyme, including Dkk2 and Osr2, and synergizes with Msx1 to activate mesenchymal odontogenic potential for tooth morphogenesis and sequential tooth formation.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Bmp4-Msx1 signaling and Osr2 control tooth organogenesis through antagonistic regulation of secreted Wnt antagonists.Dev Biol. 2016 Dec 1;420(1):110-119. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Oct 3. Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27713059 Free PMC article.
-
Activin and Bmp4 Signaling Converge on Wnt Activation during Odontogenesis.J Dent Res. 2017 Sep;96(10):1145-1152. doi: 10.1177/0022034517713710. Epub 2017 Jun 12. J Dent Res. 2017. PMID: 28605600 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Osr2 Partially Rescues Tooth Development in Runx2 Mutant Mice.J Dent Res. 2015 Aug;94(8):1113-9. doi: 10.1177/0022034515583673. Epub 2015 Apr 27. J Dent Res. 2015. PMID: 25916343 Free PMC article.
-
Genes affecting tooth morphogenesis.Orthod Craniofac Res. 2007 Aug;10(3):105-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-6343.2007.00395.x. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2007. Corrected and republished in: Orthod Craniofac Res. 2007 Nov;10(4):237-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-6343.2007.00407.x. PMID: 17651126 Corrected and republished. Review.
-
Genes affecting tooth morphogenesis.Orthod Craniofac Res. 2007 Nov;10(4):237-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-6343.2007.00407.x. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2007. PMID: 17973693 Review.
Cited by
-
Different Responsiveness of Alveolar Bone and Long Bone to Epithelial-Mesenchymal Interaction-Related Factor.JBMR Plus. 2020 Jun 21;4(8):e10382. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10382. eCollection 2020 Aug. JBMR Plus. 2020. PMID: 32803111 Free PMC article.
-
Premature primary tooth eruption in cognitive/motor-delayed ADNP-mutated children.Transl Psychiatry. 2017 Feb 21;7(2):e1043. doi: 10.1038/tp.2017.27. Transl Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28221363 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study of primary tooth eruption identifies pleiotropic loci associated with height and craniofacial distances.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Sep 15;22(18):3807-17. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt231. Epub 2013 May 23. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23704328 Free PMC article.
-
BMP4 mutations in tooth agenesis and low bone mass.Arch Oral Biol. 2019 Jul;103:40-46. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2019.05.012. Epub 2019 May 15. Arch Oral Biol. 2019. PMID: 31128441 Free PMC article.
-
Remission for Loss of Odontogenic Potential in a New Micromilieu In Vitro.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 6;11(4):e0152893. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152893. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27050091 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aberg T., Wozney J., Thesleff I. (1997). Expression patterns of bone morphogenetic proteins (Bmps) in the developing mouse tooth suggest roles in morphogenesis and cell differentiation. Dev. Dyn. 210, 383–396 - PubMed
-
- Andl T., Ahn K., Kairo A., Chu E. Y., Wine-Lee L., Reddy S. T., Croft N. J., Cebra-Thomas J. A., Metzger D., Chambon P., et al. (2004). Epithelial Bmpr1a regulates differentiation and proliferation in postnatal hair follicles and is essential for tooth development. Development 131, 2257–2268 - PubMed
-
- Bei M., Kratochwil K., Maas R. L. (2000). BMP4 rescues a non-cell-autonomous function of Msx1 in tooth development. Development 127, 4711–4718 - PubMed
-
- Chai Y., Jiang X., Ito Y., Bringas P., Jr, Han J., Rowitch D. H., Soriano P., McMahon A. P., Sucov H. M. (2000). Fate of the mammalian cranial neural crest during tooth and mandibular morphogenesis. Development 127, 1671–1679 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

