A visible dominant marker for insect transgenesis
- PMID: 23250425
- PMCID: PMC3535423
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2312
A visible dominant marker for insect transgenesis
Abstract
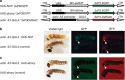
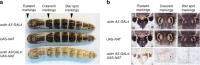
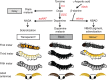
Transgenesis of most insects currently relies on fluorescence markers. Here we establish a transformation marker system causing phenotypes visible to the naked eye due to changes in the color of melanin pigments, which are widespread in animals. Ubiquitous overexpression of arylalkylamine-N-acetyl transferase in the silkworm, Bombyx mori, changes the color of newly hatched first-instar larvae from black to a distinctive light brown color, and can be used as a molecular marker by directly connecting to baculovirus immediate early 1 gene promoter. Suppression of black pigmentation by Bm-arylalkylamine-N-acetyl transferase can be observed throughout the larval stages and in adult animals. Alternatively, overexpression in another gene, B. mori β-alanyl-dopamine synthetase (Bm-ebony), changes the larval body color of older instars, although first-instar larvae had normal dark coloration. We further show that ectopic Bm-arylalkylamine-N-acetyl transferase expression lightens coloration in ladybird beetle Harmonia axyridis and fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster, highlighting the potential usefulness of this marker for transgenesis in diverse insect taxa.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Disruption of an N-acetyltransferase gene in the silkworm reveals a novel role in pigmentation.Development. 2010 Dec;137(23):4083-90. doi: 10.1242/dev.053678. Development. 2010. PMID: 21062865
-
A new arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase in silkworm (Bombyx mori) affects integument pigmentation.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2015 Apr;175(7):3447-57. doi: 10.1007/s12010-015-1516-3. Epub 2015 Feb 25. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25712907
-
The red egg gene as a novel effective egg color marker for silkworm transgenesis.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2022 Apr;143:103728. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2022.103728. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35085769
-
The evolution and genetics of lepidopteran egg and caterpillar coloration.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2021 Aug;69:140-146. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2021.04.006. Epub 2021 May 21. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2021. PMID: 34030080 Review.
-
Advanced technologies for genetically manipulating the silkworm Bombyx mori, a model Lepidopteran insect.Proc Biol Sci. 2015 Jul 7;282(1810):20150487. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2015.0487. Proc Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26108630 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Pathway Analysis of Melanin Patterning in a Hemimetabolous Insect.Genetics. 2016 May;203(1):403-13. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.186684. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 26984060 Free PMC article.
-
Towards the identification of the loci of adaptive evolution.Methods Ecol Evol. 2015 Apr;6(4):445-464. doi: 10.1111/2041-210X.12324. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Methods Ecol Evol. 2015. PMID: 25937885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structures and functions of insect arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (iaaNAT); a key enzyme for physiological and behavioral switch in arthropods.Front Physiol. 2015 Apr 13;6:113. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00113. eCollection 2015. Front Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25918505 Free PMC article.
-
An essential role of acetyl coenzyme A in the catalytic cycle of insect arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase.Commun Biol. 2020 Aug 14;3(1):441. doi: 10.1038/s42003-020-01177-9. Commun Biol. 2020. PMID: 32796911 Free PMC article.
-
A deterministic genotyping workflow reduces waste of transgenic individuals by two-thirds.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 28;11(1):15325. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94288-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34321513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wimmer E. A. Innovations: applications of insect transgenesis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 4, 225–232 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Robinson A. S., Franz G. & Atkinson P. W. Insect transgenesis and its potential role in agriculture and human health. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 34, 113–120 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Atkinson P. W.& O’Brochta D. A. In Encyclopedia of Insects 2nd edn (eds Resh Vincent H. & Cardé Ring, T.) 410–416 (Academic Press, 2009).
-
- Lorenzen M. D. et al. piggyBac-mediated germline transformation in the beetle Tribolium castaneum. Insect Mol. Biol. 12, 433–440 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Kuwayama H., Yaginuma T., Yamashita O. & Niimi T. Germ-line transformation and RNAi of the ladybird beetle, Harmonia axyridis. Insect Mol. Biol. 15, 507–512 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

