Substance use is a risk factor for neurocognitive deficits and neuropsychiatric distress in acute and early HIV infection
- PMID: 23250704
- PMCID: PMC3568179
- DOI: 10.1007/s13365-012-0141-y
Substance use is a risk factor for neurocognitive deficits and neuropsychiatric distress in acute and early HIV infection
Abstract
The acute and early stages of HIV infection (AEH) are characterized by substantial viral replication, immune activation, and alterations in brain metabolism. However, little is known about the prevalence and predictors of neurocognitive deficits and neuropsychiatric disturbances during this period. The present study examined the impact of demographic, HIV disease, and substance use factors on HIV-associated neurocognitive impairment and self-reported neuropsychiatric distress among 46 antiretroviral-naive adults with median duration of infection of 75 days relative to a sample of 21 HIV seronegative (HIV-) adults with comparable demographics and risk factors. Participants were administered a brief neurocognitive battery that was adjusted for demographics and assessed executive functions, memory, psychomotor speed, and verbal fluency, as well as the Profile of Mood States, a self-report measure of neuropsychiatric distress. Odds ratios revealed that AEH participants were nearly four times more likely than their seronegative counterparts to experience neurocognitive impairment, particularly in the areas of learning and information processing speed. Similarly, AEH was associated with a nearly fivefold increase in the odds of neuropsychiatric distress, most notably in anxiety and depression. Within the AEH sample, HIV-associated neurocognitive impairment was associated with problematic methamphetamine use and higher plasma HIV RNA levels, whereas neuropsychiatric distress was solely associated with high-risk alcohol use. Extending prior neuroimaging findings, the results from this study indicate that HIV-associated neurocognitive impairment and neuropsychiatric distress are highly prevalent during AEH and are associated with high-risk substance use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

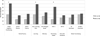
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Army Individual Test Battery. Manual of directions and scoring. Washington, D.C.: War Department, Adjutant General’s Office; 1944.
-
- Atkinson JH, Grant I. Natural history of neuropsychiatric manifestations of HIV disease. The Psychiatric Clinics of North America. 1994;17:17–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- AI-69432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DA-034362/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI090970/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI074621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 AI106039/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DA-034510/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI100665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-080353/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 MH097673/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA026306/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS083415/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AI-100665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-096113/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DA-032120/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AI-47745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- TW-008908/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- MH-097520/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA031098/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- L30 DA034362/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA-034978/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA034510/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32-DA31098/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DA034978/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI047745/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R24 TW008908/TW/FIC NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH062512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI080353/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA012065/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P01-DA12065/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- AI-74621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- MH-62512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083552/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AI-36214/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- L30 DA032120/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI096113/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30-MH62512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- AI-090970/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097520/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH-83552/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50-DA026306/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

