Oxidative stress modulates mitochondrial failure and cyclophilin D function in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
- PMID: 23250880
- PMCID: PMC3525057
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/aws292
Oxidative stress modulates mitochondrial failure and cyclophilin D function in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
Abstract
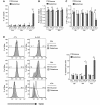
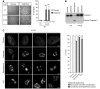
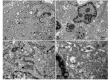
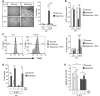
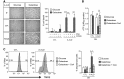
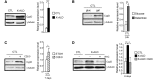
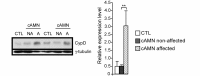
A common process associated with oxidative stress and severe mitochondrial impairment is the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, as described in many neurodegenerative diseases. Thus, inhibition of mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening represents a potential target for inhibiting mitochondrial-driven cell death. Among the mitochondrial permeability transition pore components, cyclophilin D is the most studied and has been found increased under pathological conditions. Here, we have used in vitro and in vivo models of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy to investigate the relationship between the mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening and redox homeostasis. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy is a neurodegenerative condition caused by loss of function of the peroxisomal ABCD1 transporter, in which oxidative stress plays a pivotal role. In this study, we provide evidence of impaired mitochondrial metabolism in a peroxisomal disease, as fibroblasts in patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy cannot survive when forced to rely on mitochondrial energy production, i.e. on incubation in galactose. Oxidative stress induced under galactose conditions leads to mitochondrial damage in the form of mitochondrial inner membrane potential dissipation, ATP drop and necrotic cell death, together with increased levels of oxidative modifications in cyclophilin D protein. Moreover, we show increased expression levels of cyclophilin D in the affected zones of brains in patients with adrenomyeloneuropathy, in spinal cord of a mouse model of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (Abcd1-null mice) and in fibroblasts from patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Notably, treatment with antioxidants rescues mitochondrial damage markers in fibroblasts from patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy, including cyclophilin D oxidative modifications, and reverses cyclophilin D induction in vitro and in vivo. These findings provide mechanistic insight into the beneficial effects of antioxidants in neurodegenerative and non-neurodegenerative cyclophilin D-dependent disorders.
Figures


References
-
- Baarine M, Andreoletti P, Athias A, Nury T, Zarrouk A, Ragot K, et al. Evidence of oxidative stress in very long chain fatty acid - Treated oligodendrocytes and potentialization of ROS production using RNA interference-directed knockdown of ABCD1 and ACOX1 peroxisomal proteins. Neuroscience. 2012a;213:1–18. - PubMed
-
- Baarine M, Ragot K, Athias A, Nury T, Kattan Z, Genin EC, et al. Incidence of Abcd1 level on the induction of cell death and organelle dysfunctions triggered by very long chain fatty acids and TNF-alpha on oligodendrocytes and astrocytes. Neurotoxicology. 2012b;33:212–28. - PubMed
-
- Baines CP, Kaiser RA, Purcell NH, Blair NS, Osinska H, Hambleton MA, et al. Loss of cyclophilin D reveals a critical role for mitochondrial permeability transition in cell death. Nature. 2005;434:658–62. - PubMed

