Mastoparan-induced programmed cell death in the unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
- PMID: 23250917
- PMCID: PMC3555528
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mcs264
Mastoparan-induced programmed cell death in the unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Abstract
Background and aims: Under stress-promoting conditions unicellular algae can undergo programmed cell death (PCD) but the mechanisms of algal cellular suicide are still poorly understood. In this work, the involvement of caspase-like proteases, DNA cleavage and the morphological occurrence of cell death in wasp venom mastoparan (MP)-treated Chlamydomonas reinhardtii were studied.
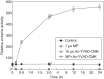
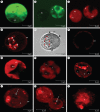
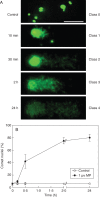
Methods: Algal cells were exposed to MP and cell death was analysed over time. Specific caspase inhibitors were employed to elucidate the possible role of caspase-like proteases. YVADase activity (presumably a vacuolar processing enzyme) was assayed by using a fluorogenic caspase-1 substrate. DNA breakdown was evaluated by DNA laddering and Comet analysis. Cellular morphology was examined by confocal laser scanning microscopy.
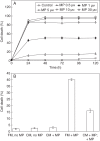
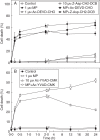
Key results: MP-treated C. reinhardtii cells expressed several features of necrosis (protoplast shrinkage) and vacuolar cell death (lytic vesicles, vacuolization, empty cell-walled corpse-containing remains of digested protoplast) sometimes within one single cell and in different individual cells. Nucleus compaction and DNA fragmentation were detected. YVADase activity was rapidly stimulated in response to MP but the early cell death was not inhibited by caspase inhibitors. At later time points, however, the caspase inhibitors were effective in cell-death suppression. Conditioned medium from MP-treated cells offered protection against MP-induced cell death.
Conclusions: In C. reinhardtii MP triggered PCD of atypical phenotype comprising features of vacuolar and necrotic cell deaths, reminiscent of the modality of hypersensitive response. It was assumed that depending on the physiological state and sensitivity of the cells to MP, the early cell-death phase might be not mediated by caspase-like enzymes, whereas later cell death may involve caspase-like-dependent proteolysis. The findings substantiate the hypothesis that, depending on the mode of induction and sensitivity of the cells, algal PCD may take different forms and proceed through different pathways.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Involvement of ethylene and nitric oxide in cell death in mastoparan-treated unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Cell Biol Int. 2010 Feb 22;34(3):301-8. doi: 10.1042/CBI20090138. Cell Biol Int. 2010. PMID: 19947911
-
The Cytotoxic Effects of Camptothecin and Mastoparan on the Unicellular Green Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2017 Nov;64(6):806-819. doi: 10.1111/jeu.12413. Epub 2017 Apr 20. J Eukaryot Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28337817
-
Cathepsin X is a conserved cell death protein involved in algal response to environmental stress.Curr Biol. 2025 May 19;35(10):2240-2255.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2025.03.045. Epub 2025 Apr 14. Curr Biol. 2025. PMID: 40233752
-
Phosphoinositide signalling in plant and algal responses to physiological stimuli.Biochem Soc Trans. 1995 Nov;23(4):853-6. doi: 10.1042/bst0230853. Biochem Soc Trans. 1995. PMID: 8654852 Review. No abstract available.
-
Elucidation of basal body and centriole functions in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Traffic. 2003 Jul;4(7):443-51. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2003.00104.x. Traffic. 2003. PMID: 12795689 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Autophagy in Haematococcus lacustris Cell Growth under Salinity.Plants (Basel). 2022 Jan 12;11(2):197. doi: 10.3390/plants11020197. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35050085 Free PMC article.
-
A polyyne toxin produced by an antagonistic bacterium blinds and lyses a Chlamydomonad alga.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Aug 17;118(33):e2107695118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2107695118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34389682 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the MAPK Cascade and its Relationship with Nitrogen Metabolism in the Green Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 12;21(10):3417. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103417. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32408549 Free PMC article.
-
When Unity Is Strength: The Strategies Used by Chlamydomonas to Survive Environmental Stresses.Cells. 2019 Oct 23;8(11):1307. doi: 10.3390/cells8111307. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31652831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Direct regulation of vascular smooth muscle contraction by mastoparan-7.Biomed Rep. 2014 Jan;2(1):34-38. doi: 10.3892/br.2013.179. Epub 2013 Oct 4. Biomed Rep. 2014. PMID: 24649065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andosch A, Affenzeller MJ, Lütz C, Lütz-Meindl U. A freshwater green alga under cadmium stress: ameliorating calcium effects on ultrastructure and photosynthesis in the unicellular model Micrasterias. Journal of Plant Physiology. 2012;169:1489–1500. - PubMed
-
- Beers EP, McDowell JM. Regulation and execution of programmed cell death in response to pathogens, stress and developmental cues. Current Opinion in Plant Biology. 2001;4:561–567. - PubMed
-
- Bonneau L, Ge Y, Drury GE, Gallois P. What happened to plant caspases? Journal of Experimental Botany. 2008;59:491–499. - PubMed

